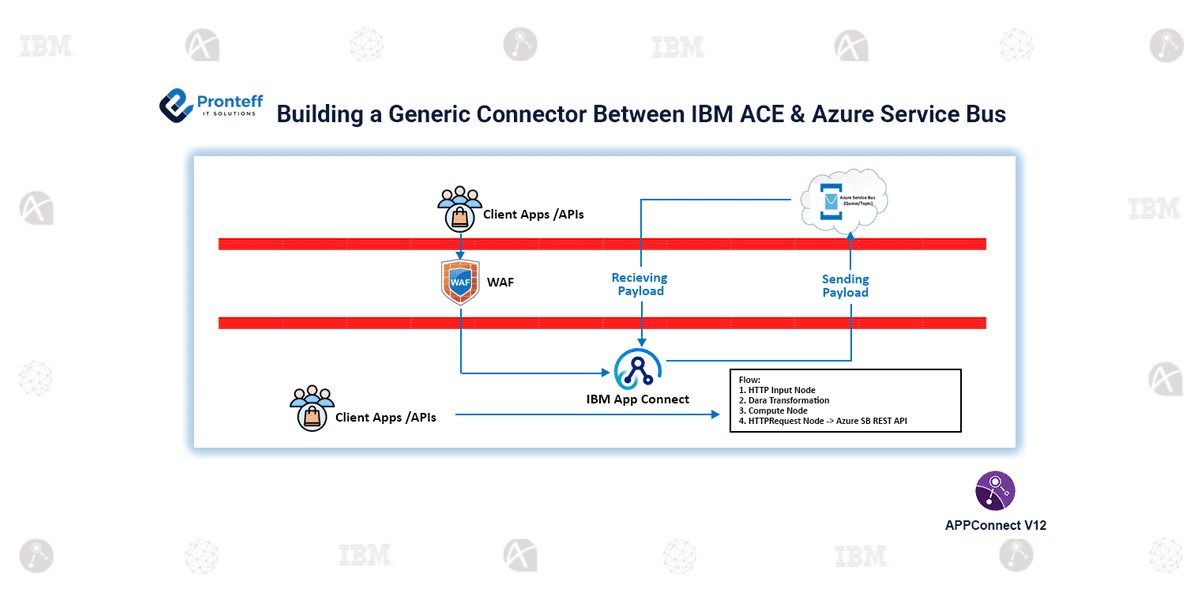
Building a Generic Connector Between IBM App Connect Enterprise (ACE) and Azure Service Bus
Here in this blog, we will learn how to build a generic connector between IBM App Connect Enterprise (ACE) and Azure Server Bus.
Introduction
In large-scale enterprise ecosystems, seamless connectivity across platforms is crucial. While IBM App Connect Enterprise (ACE) offers extensive integration capabilities, connecting it reliably to Microsoft Azure Service Bus (ASB) presented unexpected challenges.
Between unsupported JMS clients, broken connections, and connector limitations, our engineering team designed and implemented a custom, generic, and reusable connector that bridges the two worlds efficiently.
Key Highlights & Technical Insights
- Context and Motivation
- Many enterprise integration scenarios rely on robust and dynamic communication between IBM ACE and Azure Service Bus.
- Existing solutions and native connectors had limitations in flexibility, data format handling, and configuration reusability.
- To overcome these challenges, we developed a custom Java-based connector, offering a scalable, format-preserving, and queue-agnostic interface.
- Technical Challenges
- JMS Client Instability: Microsoft deprecated its JMS client (v0.9.0), causing connection failures and message backlog.
- Native Connector Limitations:
- Payloads were treated as plain text, losing JSON and binary fidelity.
- Each queue required manual setup and mapping.
- Multi-queue and dynamic routing were not natively supported.
- While IBM addressed some of these concerns later, dynamic and reusable integration remained a gap.
- Custom Generic Connector Design (JavaCompute-Based)
Our solution leverages the Azure Service Bus Java SDK within ACE’s JavaCompute nodes, offering dynamic configuration and full control over message flow.
- Receiving Payloads (Azure → ACE)
- A Scheduler node triggers periodic polling from Azure queues.
- The ReceiveFromAzure JavaCompute node:
- Fetches messages using Azure SDK.
- Extracts headers, properties, and payloads.
- Dynamically routes messages to corresponding ACE JMS queues
- Sending Payloads (ACE → Azure)
- Multiple ACE input queues forward messages to the SendToAzure JavaCompute node.
- The node:
- Dynamically determines destination queues.
- Preserves original data formats (JSON/binary).
- Includes confirmation and retry mechanisms to ensure delivery reliability.
- Solution Result
- Delivered a stable, format-preserving, and queue-agnostic integration layer.
- Eliminated dependency on deprecated JMS clients.
- Enabled dynamic, reusable configurations adaptable to multiple environments.
- Improved operational resilience and reduced manual intervention across integration pipelines.