Optimizing API Performance with IBM DataPower SLM
In this blog, we will learn how to optimize API performance with IBM Datapower SLM.
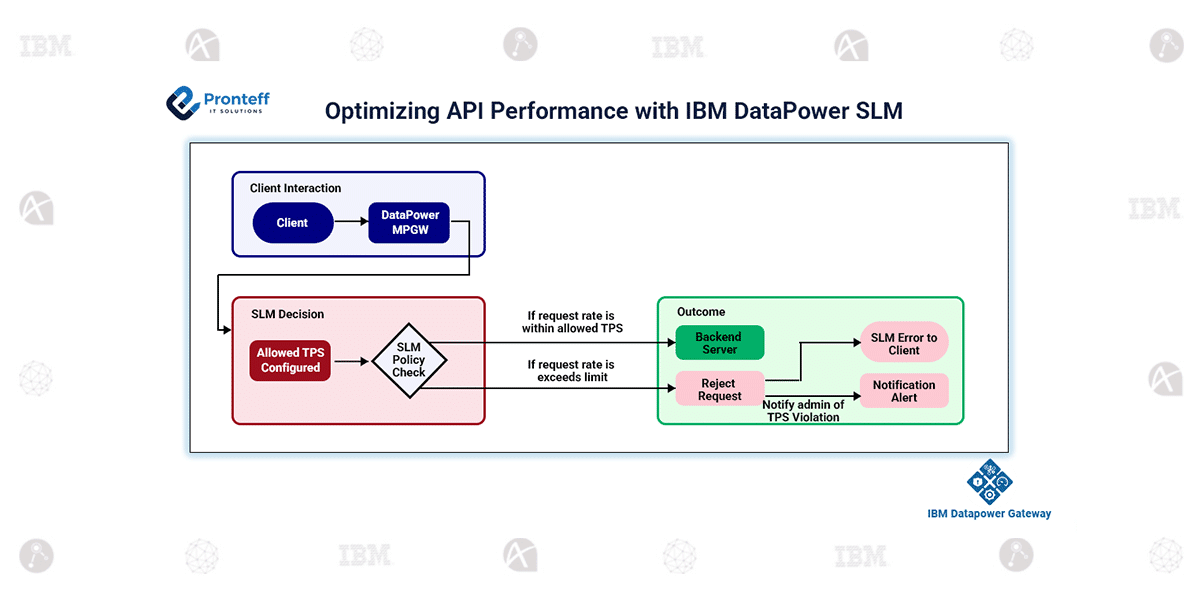
In enterprise environments, API traffic is rarely predictable. Banking systems, payment gateways, and partner platforms often experience sudden request bursts or heavy processing surges. Without proper control, backend systems may become overloaded, leading to service degradation, failures, and SLA breaches.IBM DataPower’s Service Level Monitoring (SLM) prevents this by intelligently controlling request rates, prioritizing consumers, and applying traffic protection rules — ensuring consistent, safe, and predictable API performance.
SLM Overview
SLM in IBM DataPower monitors and controls incoming requests by applying configurable rate limits and policies. It allows you to:
- Allow or deny requests based on traffic volume
- Throttle or shape traffic to maintain a steady load
- Avoid backend overload
- Ensure fair usage across clients and applications
By placing SLM inside the DataPower processing pipeline, APIs are protected even before reaching backend systems.
Key Use Cases
- Rate LimitingLimit requests per second/minute per client/application/resource to prevent abuse.
- Backend ProtectionShield fragile or legacy systems by limiting incoming load, ensuring they remain stable under pressure.
- Traffic ShapingSlow down excess traffic instead of fully rejecting it, ensuring smoother request flow.
- Burst ProtectionHandle seasonal/API spikes by rejecting or delaying traffic when configured thresholds are crossed.
- Critical Service ProtectionEnsure priority APIs get guaranteed throughput while others are controlled.
Core Capabilities
Configurable thresholds (TPS, bandwidth, count)
- Actions: Shape, Throttle, Notify
- Client & Resource classification
- Logs for hits, violations, and performance insights
- Events for monitoring and alerting
TPS Limiting Example in IBM DataPower (SLM)
Consider implementing a request-rate control (TPS limit) in IBM DataPower to protect backend services from overload.
Create & Configure MPGW:
Set up a Multi-Protocol Gateway, define a static or dynamic backend route, and attach the SLM action in the processing policy for the specific API URL match.
Define SLM Policy & Statement:
Create a new SLM Policy, and within it, add a Statement to specify:
- Interval duration (e.g., 1 second or 60 seconds)
- Threshold count (e.g., 2 requests per second)
- Action type (Throttle / Shape / Notify)
Select Action – throttle or Shape or notify:
- Throttle: Reject excess requests once the threshold is exceeded, returning an SLM fault.
- Shape: Gradually slow down traffic, allowing smoother flow instead of hard rejections.
- Notify: Log the threshold breach without affecting traffic flow — useful for monitoring
Deploy and Test: Use Postman to call the API with both regular and sporadic traffic. Normal calls are processed successfully, while excess traffic is either rejected or delayed based on configuration.