Caching and Persistence in APIGEE
In this blog, we will learn about Caching and Persistence in APIGEE.
In modern API ecosystems, performance and scalability are critical. Apigee simplifies these challenges by offering powerful, policy-driven caching mechanisms that reduce latency, minimize backend calls, and improve user experience.
Leveraging its built-in policies and internal frameworks, Apigee offers a robust caching mechanism that efficiently manages persistent data across sessions, enhancing API performance and reducing backend load.
Caching:
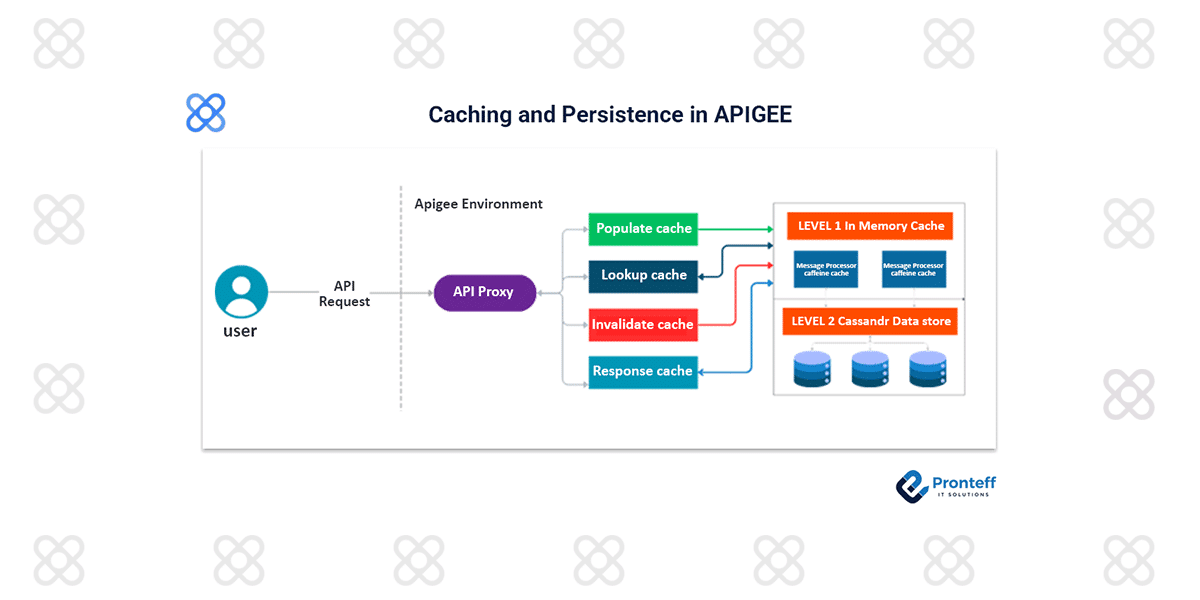
When a cache policy is executed, Apigee dynamically creates environment-scoped cache resources, ensuring isolated and consistent data management across environments. Apigee provides a range of cache policies designed to enhance performance and reduce backend load by storing and reusing frequently accessed data..
- Lookup Cache policy
- Invalidate Cache policy
- Populate the Cache policy
- Response Cache policy
Cached items are first stored in in-memory L1 cache (Caffeine) for one second— a fixed, non-configurable duration—before being persisted to the L2 cache (Cassandra), where they remain until expiry. Only the cache item’s time-to-live (TTL) and scope can be configured through the policy.
Each configured scope includes two stages of caching. They are as follows.
- Level 1 (L1) is a high-speed in-memory cache optimized for ultra-fast data access. Every message processing node has its own in-memory cache for getting the fastest responses.
- Level 2 (L2) cache operates as a durable and persistent storage layer that underlies the in-memory caching tier, offering a dependable fallback mechanism and maintaining data availability beyond the lifespan of volatile memory entries.
In Apigee, caching is handled through a seamless integration of both in-memory and persistent storage layers. Rather than treating these tiers as separate entities, Apigee presents them as a unified caching system. Behind the scenes, Apigee intelligently manages the interaction between these layers, optimizing performance through quick access to in-memory data while ensuring durability and consistency by coordinating with the persistent cache when needed.
Benefits of using Cache:
- To minimize traffic and improve latency, as the requests are fulfilled in a shorter time and with reused representations.
- Cached data is persistently maintained across transaction boundaries, enabling the consistent reuse of session-specific information across multiple HTTP requests..
- Supports security by scoping cache access to a specific environment or API proxy, ensuring controlled visibility of cached data.
The ResponseCache policy stores backend responses to reduce redundant requests, making it especially effective when backend data updates are infrequent. We can also configure to consider certain http headers and take actions accordingly.
At runtime, the PopulateCache, LookupCache, and InvalidateCache policies handle storing, retrieving, and clearing cache entries by moving data between proxy variables and the configured cache. We can persist any object that our Api requires across multiple different request/ response sessions.
Whether you’re developing a high-traffic public-facing API serving millions of users or fine-tuning internal microservices within a distributed architecture, Apigee’s caching capabilities play a crucial role in enhancing API performance and reliability.