Distributed Variables in IBM API Connect
Here in this blog, we will learn about distributed variables in IBM API Connect.
What Are Distributed Variables?
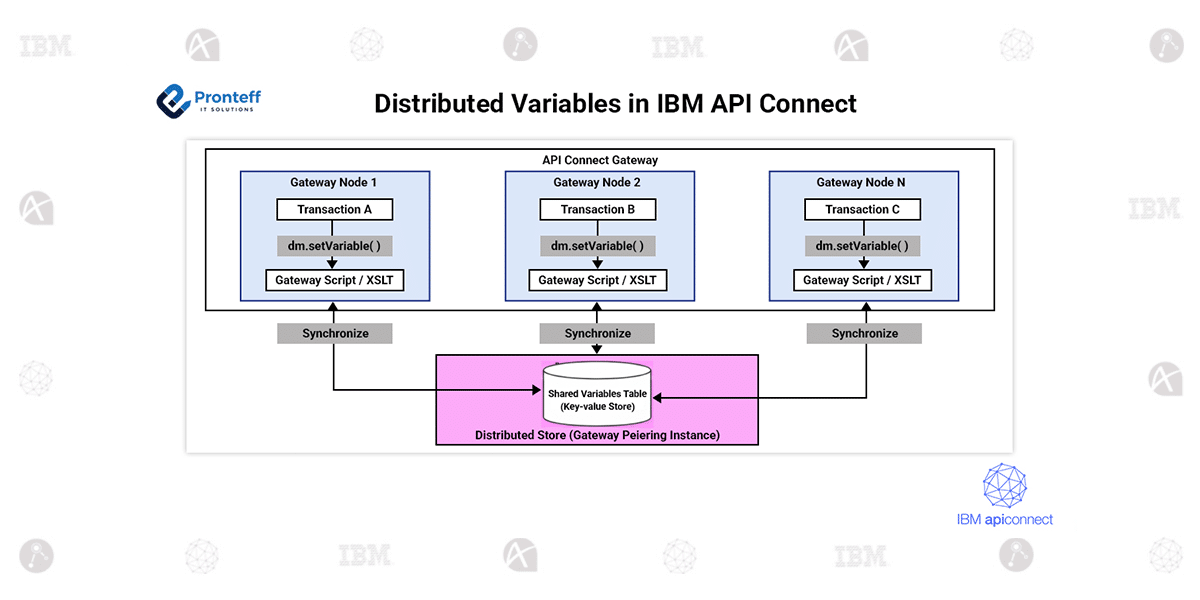
Distributed variables provide a way to centrally store and manage data within the distributed store, which resides in the gateway-peering instance. Unlike system variables that are limited to a specific transaction or domain, distributed variables offer a global scope, allowing multiple DataPower services to access and share the same data reliably.
These variables are especially useful for scenarios such as:
- Maintaining global counters across transactions
- Storing session or transactional information
- Synchronizing configurations across multiple API gateways
Key Features
- Cross-Transaction Sharing: Values can be accessed across different transactions.
- Cross-Domain Accessibility: Variables are available across multiple domains in a peer environment.
- Extension of System Variables: Distributed variables complement system variables by providing global access.
- Versatile Management: Variables can be created, retrieved, updated, or deleted using GatewayScript APIs, global commands, or XSLT.
- Shared State Management: Ideal for global counters, flags, or shared runtime data.
Steps to Set Up Distributed Variables
To enable distributed variables, you need to set up a gateway-peering instance to act as the distributed store. This setup ensures all variables are synchronized across a group of peered DataPower services.
Configuration steps:
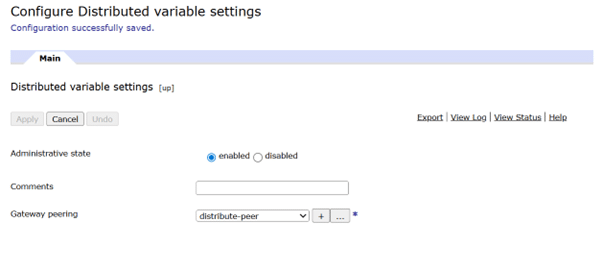
- In the DataPower gateway search bar, type Distributed Variables Settings.
- Select Distributed Variables Settings from the results.
- Configure the basic properties:
- Enable the Administrative State
- Select the Gateway Peering instance
- Choose the gateway-peering instance that will synchronize the distributed variables.
- Click Apply to update the running configuration.
- Click Save to persist these changes.
Managing Distributed Variables
Use the distributed-metadata module to create, access, delete, and manage distributed variables stored in the distributed store.
- Using GatewayScript APIs (dm.getVariable(), dm.setVariable(), dm.delVariable())
- Using Global Commands (set-dist-var, get-dist-var, delete-dist-var)
- Using XSLT Extension Elements (dp:set-dist-variable, dp:get-dist-variable(), dp:delete-dist-variable)
Common Use Cases for Distributed Variables
- Dynamic Rate Limiting
Distributed variables allow you to adjust rate limits dynamically while the APIs are in use. You can update the limit values without modifying API policies or redeploying APIs, enabling flexible traffic control across all gateways. - Global Metrics and Activity Tracking
Use distributed variables to maintain shared counters for tasks such as API usage tracking, login attempts, or feature consumption. These counters remain consistent across transactions and multiple gateways. - Lightweight Caching
Store frequently accessed small data items like flags, identifiers, short responses, or lookup values in distributed variables. This reduces repeated backend calls and improves overall performance. - Shared State Across Domains
When multiple domains require access to the same information, distributed variables provide a centralized storage solution. This eliminates duplication and ensures data consistency across domains. - Workflow and Service Coordination
Distributed variables help synchronize state across different API flows. They can be used to share tokens, workflow markers, or control flags between gateways or services, simplifying inter-service coordination.