RBI Compliance in Banking with HashiCorp Vault
In this blog, we will learn about RBI Compliance in Banking with Hashicorp Vault.
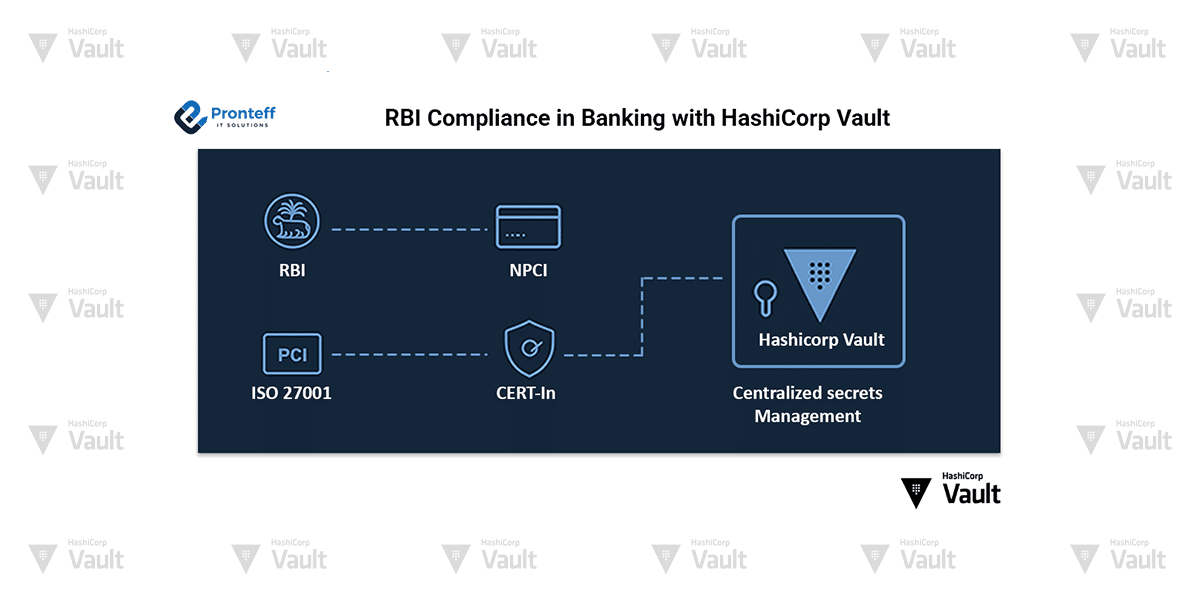
In the fast-evolving Indian banking ecosystem, data security and compliance aren’t just best practices—they are legal imperatives.
Regulatory bodies like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), NPCI, and global standards such as PCI-DSS and ISO 27001 set strict mandates for managing sensitive financial data.
For banks, secrets management—including API keys, database credentials, certificates, and encryption keys—forms the backbone of compliance.
HashiCorp Vault helps banks meet these requirements while enabling agility and automation in IT operations.
Regulatory Landscape for Indian Banks
- RBI Cyber Security Framework for Banks – mandates encryption of sensitive data at rest and in transit, with strong key management and logging.
- RBI Master Direction on Digital Payment Security Controls – requires secure handling of application secrets and API keys.
- PCI-DSS – for cardholder data protection, requiring periodic key rotation and restricted access.
- ISO 27001 / 27701 – focuses on information security management systems and privacy protection.
- CERT-In Guidelines – mandates incident logging, forensic readiness, and timely breach reporting.
Compliance Gaps Banks Often Face
- Hardcoded credentials in applications and scripts.
- No centralized visibility over key usage.
- Inconsistent rotation of credentials and certificates.
- Lack of audit trails for regulatory audits.
How HashiCorp Vault Enables Compliance
- Centralized Secrets Management – Store and access secrets from a secure, encrypted Vault instead of files or spreadsheets, and enforce RBAC and MFA.
- Automated Key Rotation – Rotate database passwords, API keys, and certificates on demand or on schedule.
- Encryption as a Service – Use the Transit Secrets Engine to encrypt/decrypt without exposing keys.
- Certificate Lifecycle Management – Automate issuing, renewal, and revocation of SSL/TLS certificates.
- Comprehensive Auditing & Logging – Immutable logs for every access and operation, integrable with SIEM.
Technical Banking Use Case – RBI Data Encryption Compliance
Scenario: A bank’s internet banking application stores customer KYC data (Aadhaar number, PAN) in the database.
RBI mandates encryption at rest for such sensitive fields.
Vault Implementation:
- Configure Vault Transit Engine for encryption-as-a-service.
- Application sends Aadhaar/PAN to Vault API for encryption before storing in the database.
- Ciphertext is stored in DB; decryption happens only when required, by authorized microservices.
- Access is controlled by Vault policies, ensuring only KYC microservices can decrypt.
- Audit logs track every encryption and decryption request for regulatory inspection.