XML Threat Protection Policy in Apigee
In this blog, we will learn about the XML Threat protection policy in Apigee.
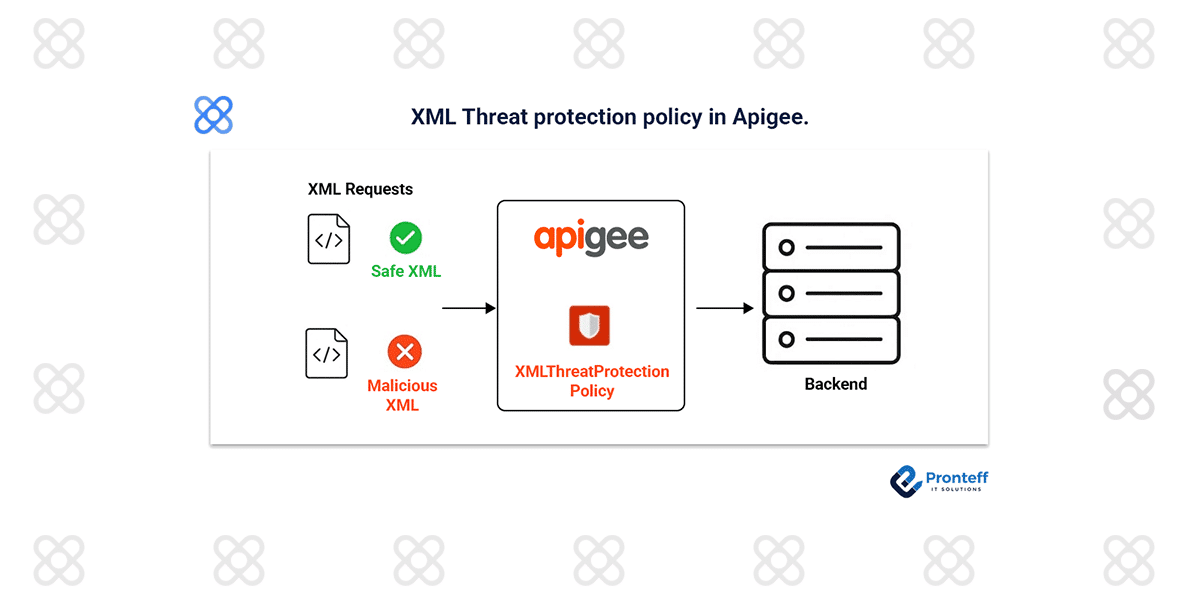
APIs frequently exchange data in XML format, which, while powerful, can also introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly validated. Malicious actors may attempt to exploit XML processing weaknesses to launch attacks such as XML bombs, entity expansion, or payload flooding. Apigee includes a native XML Threat Protection policy that helps block potential risks and ensures only secure, well-formed XML requests are passed to backend systems.
XML Threat Protection Policy:
The XML Threat Protection policy in Apigee enforces restrictions on incoming XML messages to prevent malicious or resource-intensive content from being processed. By applying constraints such as maximum depth, element count, and payload size, the policy protects APIs against a variety of XML-based attacks. It acts as the first line of defense, ensuring harmful payloads are blocked at the edge before they impact backend services.
XML Threats Addressed
Some common attack patterns that the policy mitigates include:
- XML Bombs (Billion Laughs Attack): Payloads designed to expand massively during parsing, exhausting CPU and memory.
- Excessive Nesting: Deeply nested XML structures that overload processing resources.
- Oversized Payloads: Very large XML documents are used to cause denial of service.
- Entity Expansion Attacks: Malicious use of XML entities to trigger exponential growth in data.
- External Entity Injection (XXE): Attempts to access unauthorized external resources via XML entities.
Best Practices for Using XML Threat Protection
- Define Realistic Limits: Set thresholds (size, depth, element count) based on typical payloads.
- Layer Security: Combine XML Threat Protection with OAuth, Quota, and Spike Arrest for comprehensive defense.
- Monitor Rejected Requests: Use Apigee Analytics to track enforcement and refine thresholds.
- Apply at Proxy or Shared Flow Level: For consistent protection across multiple APIs.
Conclusion
The XML Threat Protection Policy in Apigee provides a robust safeguard for APIs dealing with XML payloads. By detecting and blocking malicious or malformed requests at the gateway, it ensures backend stability, improves API resilience, and enhances overall security. When combined with other Apigee policies like Quota and Spike Arrest, XML Threat Protection becomes part of a layered defense strategy, protecting APIs from both traffic surges and malicious payloads.