Implement an automated RHEL upgrade process that fails fast
In this blog, we will learn how to implement an automated RHEL upgrade process that fails fast.
More than two years ago, we shared our approach to automating in-place upgrades for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). Since then, organizations across industries have used this structured, automated method to upgrade hundreds of thousands of systems successfully. What began as an experiment has evolved into a proven, scalable strategy for modernizing RHEL environments.
In this article, we revisit the core capabilities that enable large-scale RHEL upgrade automation, highlight what has delivered the most value, and share the practical lessons learned along the way.
The core takeaway
Fail fast, learn quickly, and repeat.
This mindset removes much of the fear traditionally associated with operating system upgrades by enabling fast recovery and minimizing risk when issues arise.
The Challenge: Legacy RHEL Environments and Technical Debt
Many enterprises today operate massive RHEL estates that have been built up over decades. While virtualization and containerization initiatives have helped modernize portions of these environments, a significant number of workloads still run on long-lived, manually maintained systems.
These “pet” servers often carry years of undocumented changes, custom configurations, and environmental drift. As a result, application teams are understandably cautious about upgrades. While infrastructure teams can re-platform systems relatively easily, redeploying tightly coupled applications is complex, time-consuming, and risky.
This challenge is a major reason organizations remain on older RHEL versions. Untangling years of technical debt to safely redeploy applications can be more expensive than the upgrade itself. That’s why a strategy that encourages rapid testing and learning is essential.
The bottom line
There is a simpler path to upgrading RHEL systems without re-engineering applications. When executed at scale, this approach delivers substantial cost savings and reduces operational risk across the organization.
The Solution: Automated RHEL In-Place Upgrades
Our strategy focuses on automating RHEL upgrades using Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform along with Ansible validated content. This approach supports upgrades ranging from RHEL 6 to 7 through to the latest RHEL releases, including multi-hop upgrades (such as RHEL 7 to RHEL 9) completed within a single maintenance window.
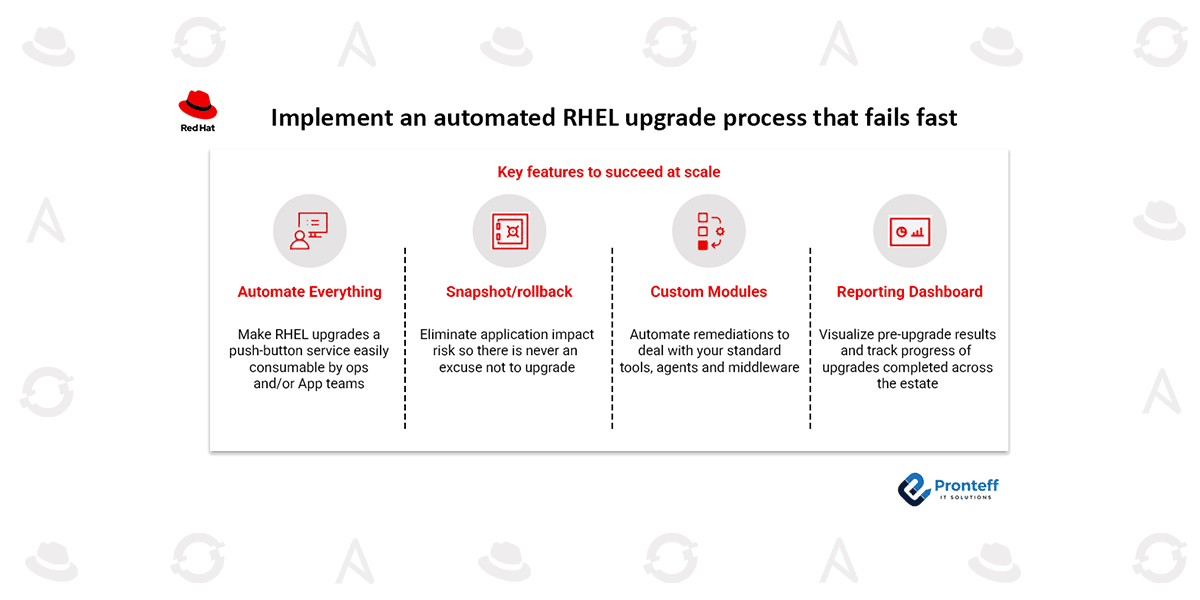
Success at scale depends on four key capabilities.
Key Features for Scalable RHEL Upgrade Automation
- End-to-end automation
Fully automated upgrade workflows transform RHEL upgrades into a repeatable, push-button service. Both infrastructure and application teams can trigger upgrades consistently, reducing manual effort and human error. - Snapshot creation and rollback
Rollback capability is the foundation of this approach. Automated snapshots—using LVM, virtualization platforms, or recovery backups—ensure that systems can be restored quickly if an upgrade does not proceed as expected. This makes it safe to experiment, fail quickly, and try again. - Custom automation modules
While the Leapp framework manages the operating system upgrade, real-world environments require additional automation. Custom modules handle third-party agents, tools, and middleware that are unique to each organization. - Upgrade reporting and dashboards
While the Leapp framework manages the operating system upgrade, real-world environments require additional automation. Custom modules handle third-party agents, tools, and middleware that are unique to each organization.
Lessons from Automating Over a Million RHEL Upgrades
One consistent lesson stands out: no upgrade process works perfectly on the first attempt. Complex environments contain unexpected configurations, third-party dependencies, and environmental quirks that cannot be predicted in advance.
Instead of trying to account for every scenario upfront, the most successful teams start upgrading early in lab and development environments.
The fail-fast approach
This methodology embraces controlled failure as a learning tool. Teams intentionally run upgrades, observe failures, roll back instantly, and refine automation based on real results. Over time, the automation becomes resilient enough to handle even the most unusual configurations.
Why Fail-Fast Works for RHEL Upgrades
Building confidence while reducing risk
Rollback capability dramatically lowers perceived risk. Application teams gain confidence knowing that systems can be restored quickly if issues occur. In regulated industries like banking, this approach has proven especially effective for meeting compliance requirements without extended outages.
Some teams even deliberately introduced failures during testing to validate rollback behavior—turning early “hiccups” into proof points rather than setbacks.
Faster automation improvement
Fail-fast testing accelerates the refinement of custom automation. Instead of guessing potential issues, teams identify real-world problems—such as missing third-party packages or incompatible agents—and automate fixes based on observed behavior.
This iterative process exposes hidden drift across environments and enables automation to adapt accordingly.
Breaking organizational resistance
Fear of failure often leads to stalled modernization efforts. Demonstrating rapid rollback and recovery helps shift the organizational mindset from risk avoidance to continuous improvement. Teams see that upgrades no longer require disruptive application redesigns.
Scaling with confidence
Organizations that adopt this approach can dramatically increase upgrade velocity. Iterative testing in non-production environments allows automation to mature before production rollout, enabling thousands of upgrades per month without widespread disruption.
Supporting Components Behind the Fail-Fast Model
- Automated snapshots and rollback using LVM, virtualization snapshots, or recovery backups
- Custom Ansible automation and Leapp extensions to manage environment-specific dependencies
- Centralized reporting dashboards to visualize findings, track progress, and identify recurring issues
Moving Forward with RHEL Upgrades
By adopting a fail-fast, automation-driven approach, large-scale RHEL upgrades become manageable, repeatable, and far less risky. What once seemed overwhelming turns into a continuous improvement process that boosts upgrade velocity and strengthens compliance.
If you’re preparing for upcoming RHEL lifecycle milestones or struggling with legacy environments, automation combined with rapid iteration is the most effective path forward.