NVIDIA GPUs and Red Hat OpenShift: Confidential containers
This blog explores how Red Hat OpenShift confidential containers, together with NVIDIA confidential GPUs, can be used to secure AI workloads on bare metal. The focus is on running Red Hat AI Inference Server as the protected workload.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has evolved far beyond experimentation and is now a driving force behind enterprise innovation. Across industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, AI enables organizations to extract insights, automate decisions, and accelerate outcomes at scale. As AI becomes more widely adopted, security risks increase in parallel. Expanding AI workloads increases the risk of unauthorized access to valuable models and the sensitive data they process.
AI models themselves are strategic assets. They embody significant investments in data collection, training, optimization, and operationalization. Protecting these assets demands more than traditional security controls that focus on data stored on disk or transmitted over networks. The most critical exposure occurs when data is actively being processed in memory—commonly referred to as data in use.
This is where confidential computing plays a transformative role. By leveraging trusted execution environments (TEEs), confidential computing protects applications through hardware-backed isolation, encryption, and cryptographic attestation. These capabilities ensure that data and code remain protected even while they are actively running. When combined with a scalable, high-performance AI and machine learning (ML) platform, confidential computing enables organizations to deploy AI securely without compromising speed, performance, or compliance—an essential requirement for regulated industries.
Confidential containers on bare metal
Confidential containers (CoCo) represent a cloud-native implementation of confidential computing that extends TEE protections to containerized workloads. Built on hardware technologies such as Intel TDX and AMD SEV-SNP, CoCo is often associated with public cloud security—but its advantages are equally compelling in on-premises, bare-metal environments, which are the primary focus of this discussion.
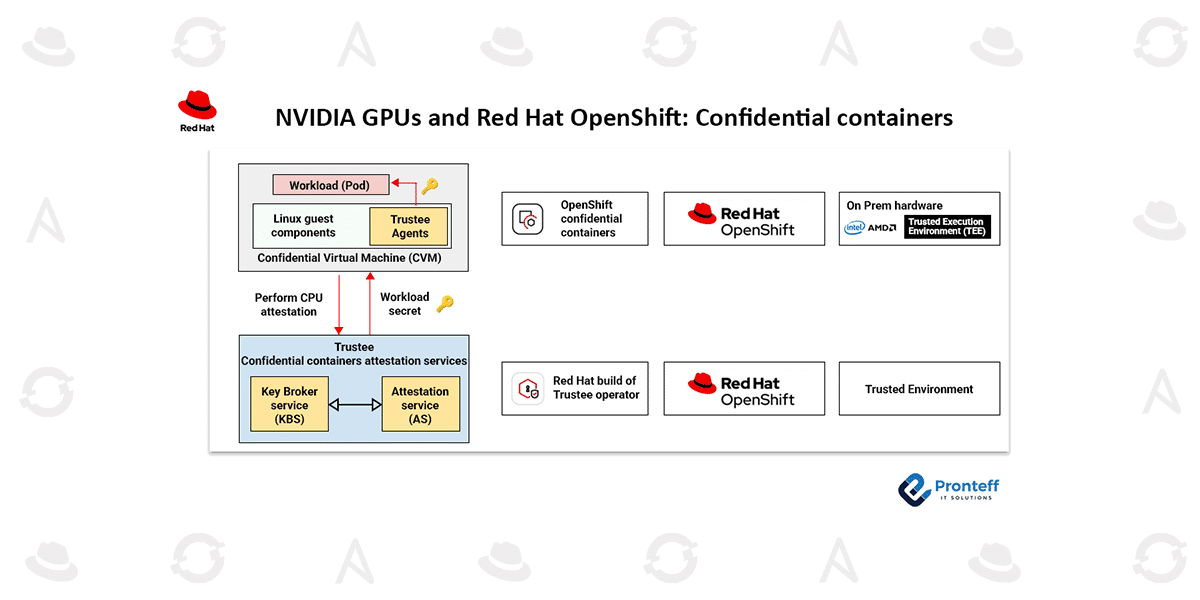
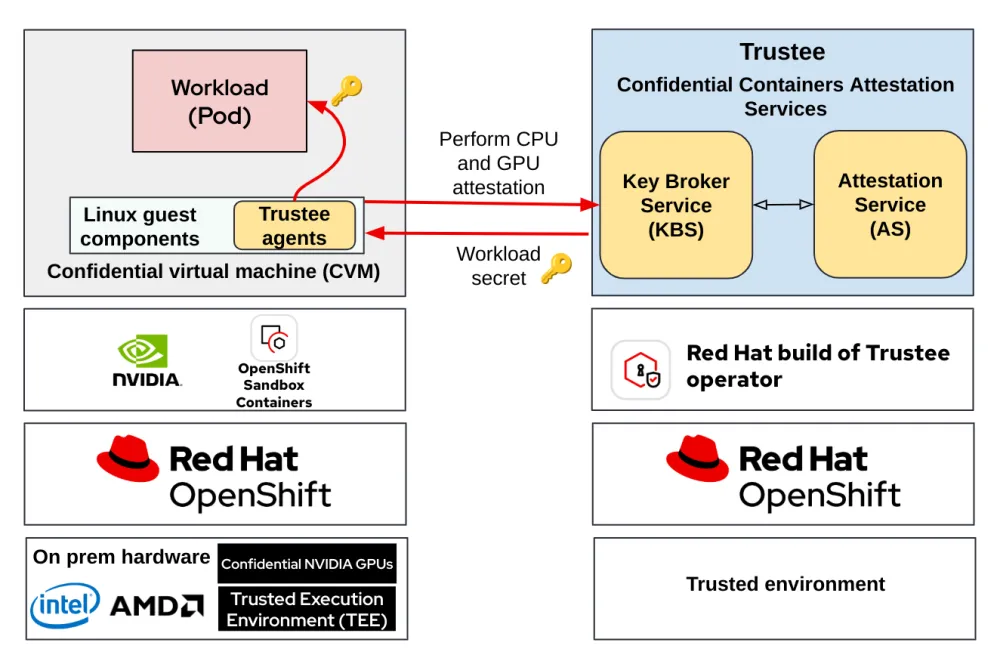
On bare metal, confidential containers address threats that originate from within the data center itself. Traditionally, once data is decrypted in memory, it becomes accessible to privileged software such as the host operating system, hypervisor, or even malicious insiders with administrative privileges. Confidential containers mitigate this risk by running workloads inside encrypted virtual machines that reside entirely within the CPU’s TEE. These encrypted VMs—known as confidential virtual machines (CVMs)—shield workloads from unauthorized inspection or modification.
To establish trust, CoCo relies on the Trustee attestation service. Trustee cryptographically verifies that the workload is running on authentic, uncompromised hardware before secrets are released to the application. This assurance enables organizations to confidently process their most sensitive workloads within their own data centers.
Red Hat OpenShift provides the foundation for this approach. As a leading hybrid cloud application platform based on Kubernetes, OpenShift delivers the scalability and orchestration capabilities required for complex AI workloads. OpenShift confidential containers extend this platform by embedding confidential computing directly into the container lifecycle.
One of the key advantages of CoCo is its simplicity. It abstracts away the complexity of the underlying hardware, allowing teams to deploy confidential workloads using standard container images and Kubernetes manifests. When a confidential container is launched, OpenShift automatically provisions a CVM within the CPU’s TEE and performs attestation through Trustee before the workload begins execution.
This architecture supports common use cases such as secure secrets retrieval by workloads running inside confidential containers. For a deeper dive into the architecture and its components, refer to the earlier blog *Introducing confidential containers on bare metal.
Extending confidential computing to GPUs
When securing AI workloads, GPUs are just as critical as CPUs. While TEEs protect data processed on the CPU, AI workloads rely heavily on GPU acceleration, creating a potential security gap when sensitive data is transferred to an unprotected GPU.
NVIDIA confidential GPUs address this challenge. CoCo is evolving to support deployments that combine confidential containers with NVIDIA confidential GPUs, including unified attestation across both CPU and GPU components.
Establishing trusted enterprise AI using NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs and confidential containers
Enterprise AI adoption depends on the ability to protect sensitive data and proprietary models across increasingly distributed environments. While confidential computing has long promised this protection, it is the convergence of NVIDIA’s advanced GPU architectures with cloud-native technologies that is making it practical at scale.
Historically, confidential computing was limited to CPUs, leaving GPU-accelerated workloads exposed. NVIDIA’s Hopper-based H100 and H200 GPUs introduced the first GPU-level confidential computing capabilities, extending hardware-backed protection to data and models processed on GPUs.
The newer Blackwell architecture advances this even further, delivering enhanced security features that meet enterprise requirements. With Blackwell GPUs, sensitive data remains protected not only at rest or in transit, but also while actively being processed on the GPU—closing a critical security gap for AI workloads.
Confidential containers as the software foundation for secure AI
While confidential GPUs secure the hardware layer, confidential containers provide the essential software abstraction that makes secure AI deployments scalable and manageable. Built on open source technologies such as Kata Containers, CoCo enables AI workloads to run inside hardened, isolated environments within Kubernetes.
Each confidential container runs inside its own lightweight CVM, protected by hardware-backed encryption. This isolation prevents access from the host operating system, hypervisor, or privileged users, significantly reducing the attack surface. For enterprises, this capability unlocks several key benefits:
- Protection of intellectual property: Proprietary AI models—including large language models such as Nemotron—can be deployed inside confidential containers, where model weights and logic remain encrypted and inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
- Data privacy and compliance: Sensitive inputs such as personally identifiable information (PII) or protected health information (PHI) can be processed securely, even on shared infrastructure.
- Secure multi-tenancy: A single Kubernetes cluster can safely host workloads from multiple teams or organizations, with each workload isolated within its own TEE.
End-to-end attestation and verifiable trust
Isolation alone is not sufficient; enterprises also need verifiable proof that workloads are running in a trusted environment. This requirement is met through composite, or end-to-end, attestation. Attestation establishes a cryptographic chain of trust that spans hardware, firmware, confidential VMs, GPUs, and container contents.
By combining NVIDIA confidential GPUs with CoCo, organizations can validate that workloads are running on genuine, uncompromised hardware with confidential computing enabled. This assurance is critical for regulated industries and is a key enabler for broader enterprise adoption of AI.
When confidential GPUs are added, the architecture evolves to include attestation for both CPU and GPU components. Trustee verifies the integrity of the CPU TEE and the secure enclave within the GPU before allowing workloads to access sensitive secrets.
Red Hat AI Inference Server in a confidential environment
Red Hat AI Inference Server is an open source, enterprise-grade solution designed to run AI models efficiently in production environments. It acts as the interface between applications and pre-trained models—particularly large language models—transforming raw model output into real business value through AI inference.
Built on the vLLM open source project, Red Hat AI Inference Server addresses common challenges associated with deploying AI at scale, including high operational costs, latency, and infrastructure complexity. Its capabilities include optimized memory management, continuous batching, model parallelism, hybrid cloud support, and compatibility with multiple accelerator types.
In essence, Red Hat AI Inference Server serves as the execution engine for enterprise AI, enabling fast, scalable, and cost-effective inference across hybrid environments.
Why run Red Hat AI Inference Server with confidential containers and GPUs?
Running Red Hat AI Inference Server inside confidential containers on bare metal delivers two primary advantages. First, it protects the intellectual property embedded in AI models by preventing unauthorized access—even from administrators with physical access to the infrastructure. Second, it safeguards sensitive input data, making it well-suited for use cases involving financial records, medical data, or other regulated information.
This approach allows organizations to retain full control over their on-premises infrastructure while achieving security guarantees comparable to—or exceeding—those of public cloud environments. Trustee attestation plays a central role by validating that both the CPU and GPU environments remain untampered.
When deployed in this configuration, the AI inference workload runs inside a confidential pod. Secrets—such as encryption keys used to decrypt the model—are only released after successful attestation.
Key value areas of confidential AI inference
Deploying Red Hat AI Inference Server with confidential containers and confidential GPUs delivers value across three critical dimensions:
- Protection of data in use: The entire inference pipeline—models, input data, and outputs—is protected within TEEs and confidential GPUs, shielding it from privileged or malicious software.
- Preservation of intellectual property: Proprietary models remain encrypted and protected from theft, tampering, or reverse engineering, enabling secure collaboration and innovation.
- End-to-end pipeline security: Confidential GPUs extend protection from the CPU to the GPU, ensuring encrypted communication and secure execution across the entire AI stack.
Final thoughts
As AI becomes increasingly embedded in enterprise operations, security requirements will continue to rise. Confidential computing—enabled by NVIDIA confidential GPUs and orchestrated through Red Hat OpenShift confidential containers—offers a comprehensive answer to these challenges. This approach establishes a new standard for secure AI, allowing organizations to innovate with confidence while maintaining privacy, compliance, and control.