Discover the Ansible Lightspeed AI Assistant
In this blog, we will learn how to discover the Ansible Lightspeed AI Assistant.
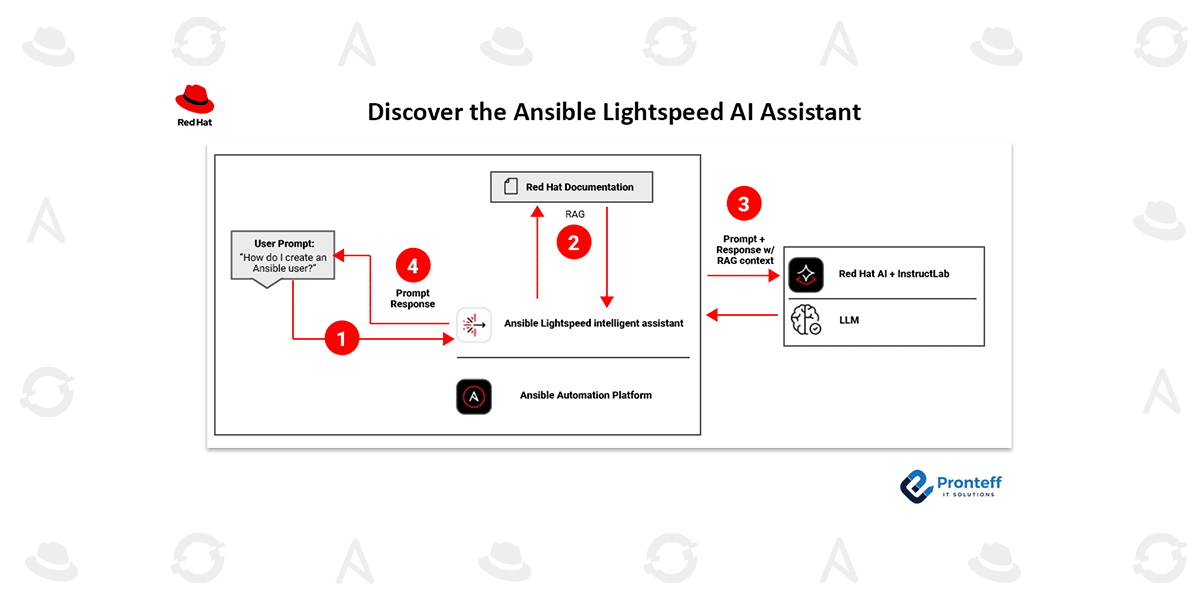
Earlier this year, we introduced the Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant, a generative AI capability designed to enhance the Ansible Automation Platform experience. Built as an embedded conversational interface, it functions like having an Ansible expert available on demand. By surfacing relevant documentation directly inside the platform, the assistant accelerates troubleshooting, simplifies onboarding, and supports the daily administration of automation environments.
The assistant is fully integrated into the Ansible Automation Platform dashboard, allowing users to interact with it without leaving their operational workspace. Administrators and operators can view platform insights—such as resource counts, job activity trends, and recent project updates—while simultaneously engaging the assistant through a side-panel chat interface.
Elevating the platform experience with generative AI
The intelligent assistant reflects a broader initiative across product and engineering teams to modernize and streamline the user experience. Recent platform advancements include:
- A more unified and simplified user interface
- Self-service automation capabilities for broader user empowerment
- An on-premises analytics dashboard for performance visibility
- Expanded automation collections for platform management
Together, these innovations are designed to reduce operational complexity and make automation more accessible across organizations.
Building on the Ansible Lightspeed foundation
When Red Hat first launched Ansible Lightspeed with IBM WatsonX Code Assistant in 2023, the focus was on developer productivity. The coding assistant helped engineers generate and refine Ansible playbooks, roles, and tasks more efficiently. Enhancements such as content explanations, source attribution, and prompt guidance improved transparency and usability.
Powered by IBM Granite code models and trained on Ansible-specific datasets, the solution lowered the barrier to entry for automation development, enabling new users to learn Ansible syntax and best practices faster.
The intelligent assistant extends these benefits beyond content creation to platform operations. By minimizing context-switching and “swivel-chair” workflows, administrators can research issues, understand configurations, and resolve problems directly within the platform interface.
Example questions the assistant can handle
Users can engage the assistant with practical operational queries such as:
- “What is an execution environment?”
- “How do I manage user access in Ansible Automation Platform?”
- “Explain the ‘ERROR! couldn’t resolve module/action’ message.”
- “How do I configure Event-Driven Ansible?”
Using a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) architecture connected to Red Hat documentation and knowledge sources, the assistant also returns cited references so users can explore topics in greater depth.
What’s coming next
Future enhancements will expand the assistant’s data integrations to include automation performance and health insights. This will enable more advanced operational prompts, for example:
- “Why did my ‘VM-migration’ automation job fail?”
- “List all inventories in my Ansible Automation Platform deployment.”
- “What is the current status of running jobs?”
These capabilities aim to transform the assistant from a knowledge guide into a real-time operational advisor.
Getting started
To enable the Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant, organizations need:
- An active Ansible Automation Platform subscription
- A deployed large language model (LLM) hosted on Red Hat AI or a supported bring-your-own-model configuration, as outlined in Red Hat documentation
For detailed installation and configuration guidance, refer to the official product documentation.