IBM MQ dead letter queue alerts
In this blog, we will learn about IBM MQ dead letter queue alerts.
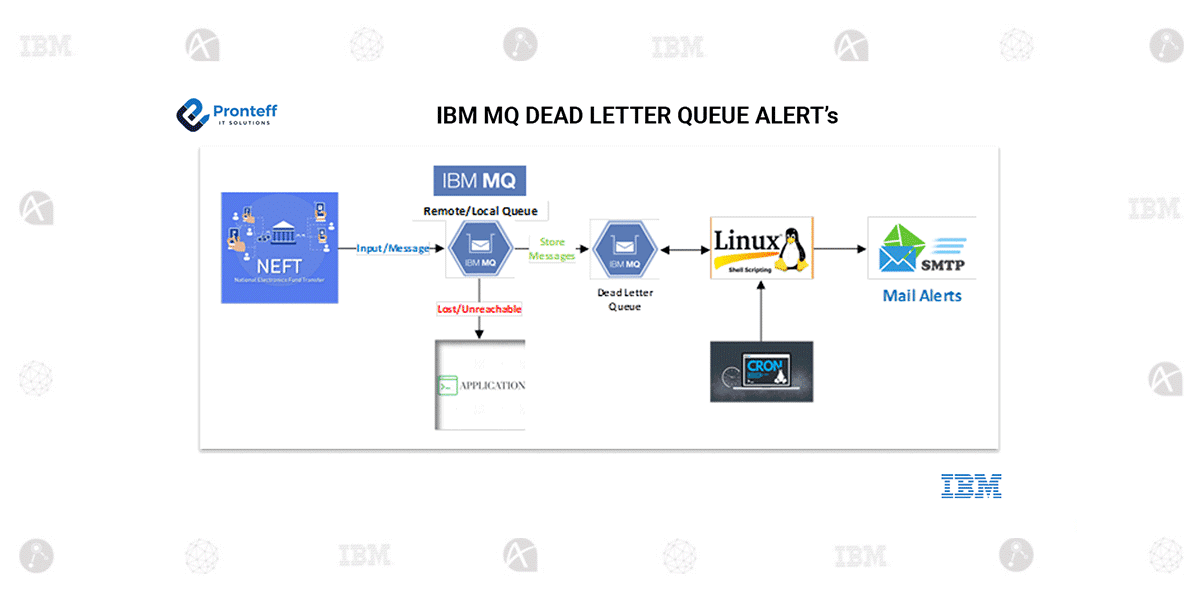
A message processing and alerting system using IBM MQ for handling messages, a Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) for failed messages, and Linux shell scripting with cron jobs for generating email alerts via SMTP.
Flow of the Diagram:
Message Input (NEFT System) → IBM MQ Queue:
The National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) system generates messages related to fund transfers.
These messages are sent to IBM MQ (a message-oriented middleware) via a Remote/Local Queue.
The queue acts as a buffer, storing and forwarding messages to the application for further processing.
IBM MQ Processing & Message Handling:
If the receiving Application is available, the messages are processed successfully.
If the application is unreachable or fails to process the messages, they are lost and redirected to a Dead Letter Queue (DLQ).
Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) Monitoring:
Unprocessed or failed messages are stored in a DLQ, which acts as a holding area for problematic messages.
This ensures that messages are not lost permanently and can be reprocessed or investigated.
Linux Shell Script Execution:
A Linux-based shell script is used to monitor the DLQ.
This script periodically checks for messages in the DLQ and triggers alerts when messages accumulate.
Automated Cron Job Scheduling:
The script is executed at scheduled intervals using a cron job.
The cron job ensures that DLQ monitoring runs automatically without manual intervention.
SMTP Email Alerts:
If messages are found in the DLQ, an alert notification is generated.
The script triggers an SMTP email to notify system administrators or support teams about the issue.
This allows for the timely implementation of corrective measures.
Key Takeaways:
IBM MQ ensures reliable message handling, storing messages until they are successfully processed.
Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) prevents message loss and allows troubleshooting of failed transactions.
Linux shell scripting with cron jobs automates monitoring, ensuring continuous system reliability.
SMTP-based email alerts notify administrators, preventing unnoticed failures.