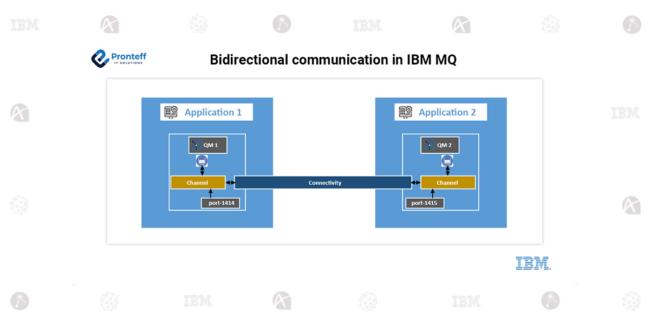
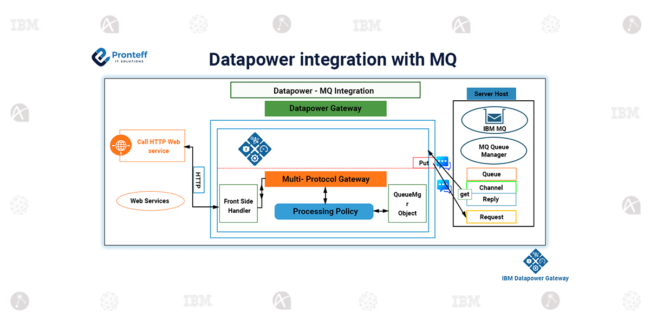
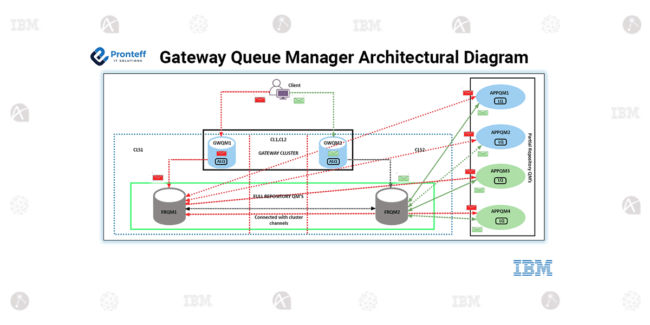
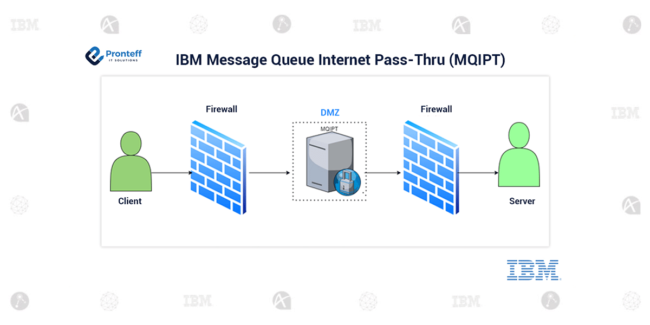
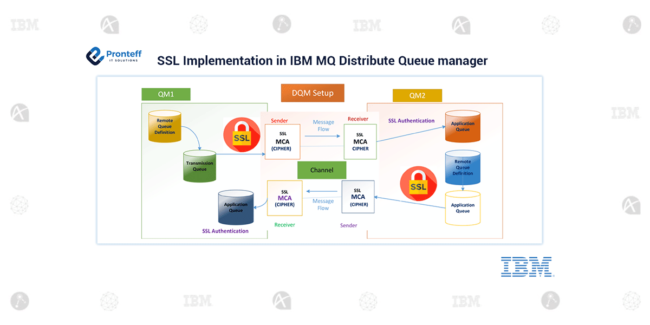
Bidirectional communication in IBM MQ
Bidirectional communication in IBM MQ Bidirectional communication in IBM MQ provides several advantages, particularly in environments that require robust, reliable, and flexible messaging systems. Here are some key benefits: Reliability and Guaranteed Delivery Message Persistence: IBM MQ ensures that messages are stored reliably and can be retrieved even after a system failure. This guarantees that…