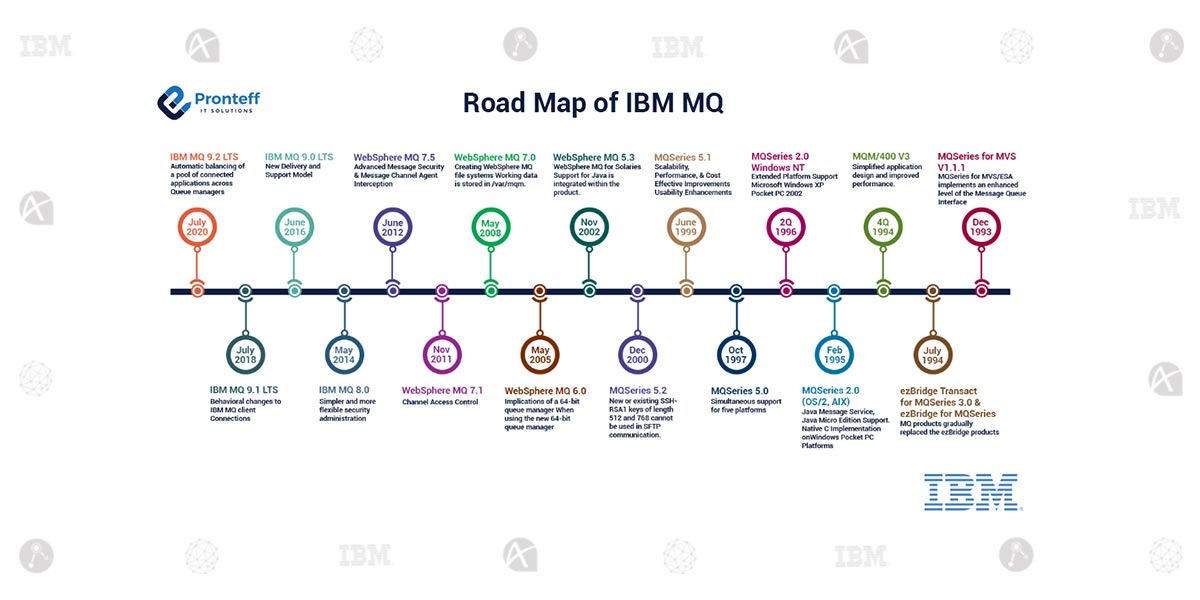
Road Map of IBM MQ
IBM MQ 9.2 LTS
Automatic balancing of a pool of connected applications across a set available Queue managers
Uniform clusters:
Uniform clusters are a specific pattern of an IBM MQ cluster that provides applications with a highly available and horizontally scaled collection of queue managers. When an application interacts with a uniform cluster as a single group, the queue managers work together to maintain an even balance of application instances across the cluster, including across queue manager maintenance and restarts.
Single set of configuration files
A single set of configuration files can be defined once and used to deploy multiple queue managers into the uniform cluster, ensuring the configuration is consistent across them.
Enhanced protection of stored passwords in MQIPT
From IBM MQ 9.2.0, all passwords that are stored in the MQIPT configuration can be protected by encrypting the passwords using the mqiptPW command.
IBM MQ 9.1 LTS
Behavioral changes to IBM MQ client Connections
There are a number of minor changes to the way in which a client channel connects to a queue manager. The changes are most specifically in the interactions between security exits and the application of CHLAUTH mapping rules.
IBM MQ 9.0 LTS
New Delivery and Support Model
IBM MQ 9.0 introduces a new delivery and support model for IBM MQ. From IBM MQ 9.0, two release types will be made available; the Long Term Support (LTS) release and Continuous Delivery (CD) release.
The Long Term Support release is a recommended product level for which support, including defect and security updates, will be provided over a specified period of time. This version is intended for systems which demand a long term deployment and maximum stability.
Continuous Delivery releases deliver new functional enhancements, in addition to fixes and security updates, on a much shorter cadence, so providing much more rapid access to those new functions. This version is intended for systems where applications want to exploit the very latest capabilities of IBM MQ
IBM MQ 8.0
Simpler and more flexible security administration.
The ability to integrate with existing identity repositories, enabling consistency across a solution and reducing security administration for solutions with many users
More flexible administration of client connection information.
Customizable publication-routing for more efficiency in large scale clusters.
The ability to separate workloads by defining multiple cluster transmission queues on all supported platform.
WebSphere MQ 7.5
Advanced Message Security
IBM IBM WebSphere MQ Advanced Message Security (AMS) is a separately installed component, which is separately charged. It provides a high level of protection for sensitive data that is flowing through the IBM WebSphere MQ network. You do not need to modify existing applications to take advantage of AMS
Message Channel Agent Interception
MCA interception feature allows a queue manager running under IBM IBM WebSphere MQ with a licensed install of Advanced Message Security to selectively enable policies to be applied for server connection channels. MCA interception allows clients that remain outside IBM WebSphere MQ AMS to still be connected to a queue manager and their messages to be encrypted and decrypted
WebSphere MQ 7.1
Channel Access Control
Block connections from specific IP addresses
Block connections from specific Userids
Set MCAUSER value used for any channel coming from a specific IP address
Set MCAUSER value used for any channel having a specific SSL or TLS DN
Set MCAUSER value used for any channel connecting from a specific QManager
Block connections claiming to be from a particular QManager unless the connection is from a specific IP address
Block connections claiming to be from a particular Client Userid unless the connection is from a specific IP address
Block connections presenting a particular SSL or TLS certificate unless the connection is from a specific IP address
WebSphere MQ 7.0
Creating WebSphere MQ file systems The installation directory for the WebSphere MQ product code is /opt/mqm. Working data is stored in /var/mqm. You cannot change these locations. The IBM Global Security Kit (GSKit) must also be installed into its default location. (The GSKit enables you to use SSL security on Windows and UNIX® systems.)
WebSphere MQ 6.0
Implications of a 64-bit queue manager When using the new 64-bit queue manager, the use of the LIBPATH and LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable is not advised. Setting these environment variables might result in you not being able to run any WebSphere MQ commands. By default, the installation will operate as in previous versions of WebSphere MQ, with symbolic links being created from /usr/lib, /usr/bin and /usr/include to the appropriate files within the WebSphere MQ tree structure. In the case of /usr/lib the symbolic links will be to the 32-bit WebSphere MQ libraries provided for customer 32-bit applications.
Using the JMS postcard application to verify a server-to-server installation. To verify that the communication between two machines, the sender of the message and the receiver, are working correctly, and that the WebSphere MQ Java messaging support is successfully installed, you can use the JMS Postcard application. Both machines must use TCP/IP.
WebSphere MQ 5.3
WebSphere MQ for Salaries
WebSphere MQ for Solaris now supports WebSphere MQ channels protected using the industry standard Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). See WebSphere MQ Security for details. This support is based on IBM Global Security Kit; a copy of this product is included with WebSphere MQ.
Support for Java is integrated within the product. This replaces the support previously provided by MQSeries Support Pac MA88.
Product documentation is now supplied on separate CD-ROMs.
Support for Web Administration and the Internet Gateway has been removed. If you have these features installed from a previous release of the product, you will lose them when you upgrade. A new form of license management is implemented for this release of the product. WebSphere MQ now supports generic authority administration.
MQSeries 5.2
The following are the list of changes introduced in the SFTP Client and Server Adapter.
New or existing SSH-RSA1 keys of length 512 and 768 cannot be used in SFTP communication.
New or existing SSH-RSA keys of length 512 and 768 cannot be used in SFTP communication.
By default, curve25519-sha256 key exchange algorithm is used.
Generation of SSH-DSS keys of length lesser than 1024 is not supported for security reasons.
Generation of SSH-RSA keys of length 512 and 768 is not supported for security reasons.
New MAC algorithms are supported and new ciphers are supported.
MQSeries 5.1
Scalability Improvements
Exploitation of dynamic workload distribution technology — MQSeries is now easier to deploy across multiple nodes and benefits from load balancing across multiple processors.
OS/2 SMP for high memory — decreases the limitations associated with OS/2 shared memory allowing more clients and applications to run alongside DB2/Comms and other high memory entities.
Increased queue size now 2 Gb — improves message throughput and allows increased message-holding memory capabilities.
Multi-threaded channels support — increases the number of clients capable of running against a Sun, AIX, or HP platform.
Performance Improvements
Dynamic workload distribution support provides efficient use of available resources, maximizing efficiency of closely linked processors.
I/O avoidance when MQGET waiting minimizes disk access.
Multi-threaded agent process enables more efficient use of resource. Multiple application processes can run in parallel, improving throughput.
Cost Effective Improvements
Automated administration provides reductions in costs associated with training and skills required in administering a cluster environment.
Recovery function within a dynamic workload distribution environment, or cluster, enables seamless failover and continued operation at minimal effort and cost to the systems administrator.
Improved application development features for administration applications.
Usability Enhancements
Faster setup and easier management of the environment.
Compatible to Microsoft™ Directions for the MQSeries for Windows NT product.
Pocket PC 2002
MQSeries 5.0
Simultaneous support for five platforms
Database-message sync point coordination (DMSC)
IBM Software Servers integration
New programming features, such as support for very large messages and files, distribution lists, and additional languages
Communication features that simplify administration, boost performance, and provide Novell SPX support
Administration and security enhancements including optional DCE connection security
New flexible price structure
Introduction of MQSeries upgrade protection with support
MQSeries 2.0 Windows NT
WebSphere MQ Everyplace V2.0 supports point-to-point messaging via JMS, and also extends Java programming to smaller devices that can run Java Micro Edition (J2ME).
Supports C and Java on Microsoft™ Windows® Pocket PC operating environments
A native C implementation is available on Windows Pocket PC, including Compaq iPAQ support. Other additions include scalability and administration improvements. Additional platforms, including Windows XP, are fully supported
Full-client queue manager function
Scalability and quality improvements
Channel improvements
Full remote support
Full accessibility and improved code page support
New trace facilities
Extended Platform Support:Platform support is enhanced with the addition of:
Microsoft Windows XP (Professional Edition)
Pocket PC 2002
MQSeries 2.0 (OS/2, AIX)
Java Message Service (JMS) Support:
Java Micro Edition (J2ME) Support:
Native C Implementation on Windows Pocket PC Platforms
Security:WebSphere MQ Everyplace provides extensive security through authentication, encryption, and compression, including:
Authentication to control access
Compression to reduce resource requirements (for transmission or storage)
Encryption to protect the contents when an object is transmitted
MQM/400 V3
Simplified application design and improved performance through distribution lists which allow a single message to be put to multiple queues
Improved programmer choice through automatic creation of channel definitions for receiver and server-connection channels
Static bindings for the ILE RPG programming language and support for Message Queuing Interface (MQI) applications written in C++ increase programmer choice
Message segmentation, ordering and grouping to improve checking of transactional data and allow more applications to use MQM/400 particularly for large transactions
Fast no persistent messages for data which needs simple, fast delivery
MQSeries V1.2
Performance
Increased maximum number of channels
Performance improvement for Get by Msgid/Correlid
Read ahead on MQGET
Reduced Path length for allocating empty pages
Reduced system overheads during message processing
New parameter to allow format of multiple page set extents
Channel Initiator Design
Support for new MQSeries Formats and Protocols
Service support
Consolidation of service updates from previous releases
Restrictions on the IMS Bridge in MQSeries for MVS/ESA V1.1.4 removed.
New service-related utilities
Synergy enhancements
Implementation of MVS Extended Console Support (EMCS)
Report Options for application acknowledgement
Auto connect to MQSeries using CICS SIT Parameter
MQSC Syntax improvements
Change of triggering rules
MQSeries Internet Gateway feature available with product
CICS DPL Bridge
MQSeries for MVS/EVS V1.1.4
IMS Bridge to simplify access from MQSeries programs to both legacy and new IMS/ESA applications.
Support for message data conversion between different code pages.
A chargeable feature allowing attachment of MQSeries Clients directly to MQSeries for MVS/ESA.
Support for a sync point mechanism with in-doubt wait handling to be provided in a future CICS for MVS/ESA release, which is currently part of a product introduction program.
A no-charge feature to support Interlink TCP/IP as well as IBM TCP/IP.
Enhancements to channel functions, including a default transmission queue.
Other improvements to the programming environment to ensure consistency with other MQSeries platforms.
MQSeries for MVS/ESA V1.1.3
Support for sending messages via the Mover (Message Channel Agent) without the use of CICS/ESA
Transmission Control Protocol/Interconnect Protocol (TCP/IP) support with new Mover, above)
Support for CICS/MVS Version 2 (with new Mover, above)
Confirmation of arrival/delivery
Message expiration
Enhanced availability (dynamic page set expansion)
Instrumentation and alerts
MQSeries for MVS/ESA V1.1.2
PL/I support
IMS trigger monitor
Accounting information
Multiple subsystem recognition characters
ezBridge for MQseries 3.0
MQ products gradually replaced the ezBridge products and as the product rapidly gained in customer acceptance (and naturally new requirements) enhancements were made that attempted to satisfy the twin goals of cross-platform functional consistency as well as specific platform exploitation where required.
ezBridge for MQSeries
ezBridge for MQSeries provided fault-tolerant, guaranteed delivery transaction messaging on 10 different hardware platforms. This product was licensed to IBM as the initial code base for IBM MQSeries (renamed WebSphere MQ and later renamed IBM MQ, which was co-developed and co-marketed with IBM
MQSeries for MVS/ESA V1.1.1
In December 1993, the Hursley Development Laboratories released a product called Message Queue Manager for MVS/ESA which joined a small family of existing products all of which were part of the new IBM MQSeries family.
IBM MQSeries for MVS/ESA is the messaging and queuing manager for the MVS/ESA environment in the Messaging and Queuing Series
MQSeries for MVS/ESA implements an enhanced level of the Message Queue Interface (MQI)
Messaging and queuing is a flexible, robust technology that insulates from the application many of the complexities of the networking environment. It is the asynchronous program-to-program interface in the Networking Blueprint.