Migration Toolkit 2.9: Speed and Efficiency for VM Moves
In this blog, we will learn about how Migration Toolkit 2.9 delivers speed and Efficiency for VM Moves.
The Migration Toolkit for Virtualization (MTV) 2.9 introduces major enhancements designed to speed up virtual machine (VM) migrations and reduce business disruption when moving workloads to Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization. A highlight of this release is the storage offloading capability, initially developed in collaboration with certified storage partner Hitachi Vantara, whose driver is the first to reach technology preview.
By shifting the data transfer process from the network layer to the storage system itself, this feature significantly reduces downtime and resource strain during cold migrations, making it especially valuable for production workloads.
Accelerating migrations with storage-driven data transfer
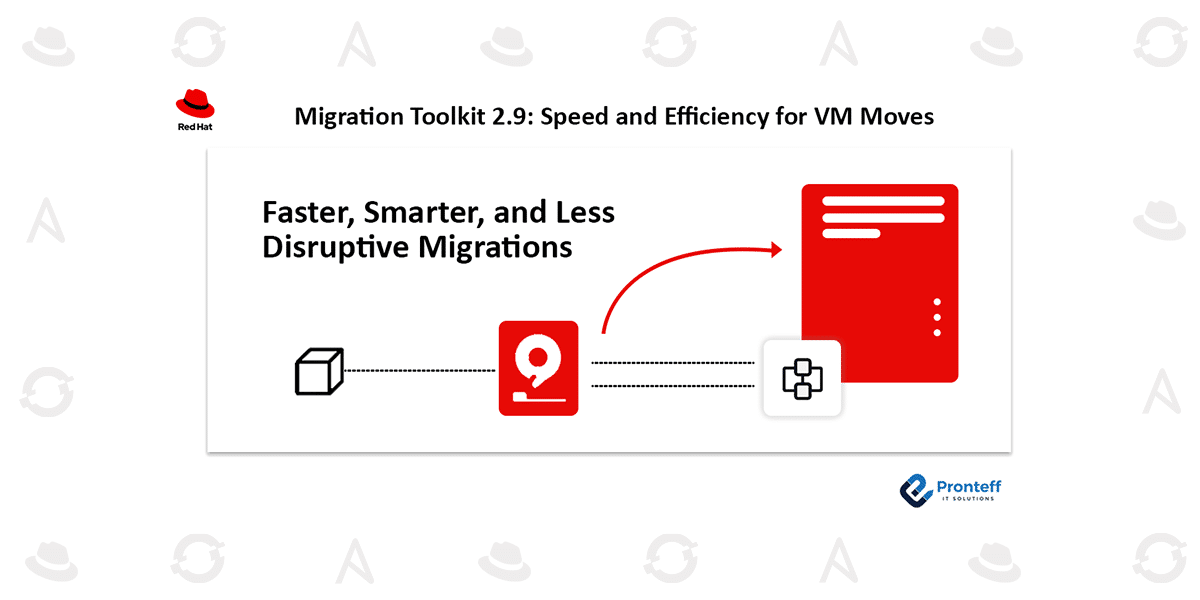
Traditionally, VM migration depends heavily on network transfers—MTV reads the source disk, sends it over the network, and writes it into the new environment. This process can be slow, network-intensive, and resource-consuming.
The new storage offloading capability shifts the responsibility of data copying to the storage system. For example, a VMware VMDK can be transformed within the array into an OpenShift Persistent Volume (PV). Once the PV is available, MTV finalizes the conversion to OpenShift Virtualization format, enabling the VM to start. The original source disk also remains intact, allowing rollback if needed.
This approach is especially beneficial for large, multi-terabyte disks, where offloading data movement directly to the storage system drastically cuts down migration time. CPU and memory resources are also preserved for active workloads since the network no longer handles the heavy lifting.
The functionality is enabled by a new storage offload plugin module, which certified storage vendors can extend through the Forklift open source community. This collaborative model ensures enterprises can optimize migrations while leveraging their existing infrastructure.
Key advantages of storage offloading
Faster migration, less downtime: Hitachi’s internal benchmarks show migration time reduced by up to 10x. A process that once required ten hours can now be completed in just one, allowing services to return online far more quickly. Support for warm migration is also on the roadmap.
Lower risk and greater reliability: Large-scale VM migrations are complex, often carrying risks of errors, extended downtime, or even data loss. By simplifying and accelerating the process, this feature reduces risks and builds confidence in migration outcomes.
Reduced network strain, improved efficiency: With disk copy operations handled by the storage array, networks and servers are freed from bottlenecks. This lets IT teams focus on other initiatives while making migrations more resource-efficient.
Hitachi Vantara’s role in enabling storage offloading
Hitachi Vantara played a pivotal role in developing this functionality and is among the first Red Hat-certified storage partners to support it. Because of their shared commitment to open source innovation, Red Hat and Hitachi have ensured that the capability is included in MTV 2.9 and openly available for organizations.
Organizations using Hitachi Vantara storage can now migrate workloads up to 10x faster, but the approach can also be extended to other storage platforms over time, ensuring broader ecosystem benefits.
Additional enhancements in MTV 2.9
Beyond storage offloading, this release introduces several improvements to address migration challenges:
Raw copy mode: Enables VMs with unsupported or incompatible guest operating systems to be migrated by performing a raw disk copy. This includes encrypted disks that can now be moved without requiring credentials.
VM name adjustments: Users can now rename non-conformant VM names directly during migration planning, reducing the risk of failures caused by naming restrictions in the target environment.
Nested virtualization retention: VM configurations that enable nested virtualization in VMware can now be preserved post-migration in OpenShift.
Modernized UI: Navigation updates, a redesigned overview page, and an improved migration plan wizard provide a smoother user experience for planning, executing, and monitoring migrations.
Summary
The MTV 2.9 release marks a major step forward for enterprises looking to modernize infrastructure by moving workloads to OpenShift Virtualization. With storage offloading at the core—accelerating migration, cutting downtime, and easing network strain—administrators gain a faster and more reliable way to move critical workloads. Combined with new features like raw copy mode, name flexibility, and UI upgrades, MTV 2.9 makes large-scale migrations simpler, safer, and more efficient.