Red Hat Lightspeed in 2025: Turning observability into automated outcomes
In this blog, we will learn how Red Hat Lightspeed in 2025 is turning observability into automation.
For years, Red Hat Lightspeed (formerly Red Hat Insights) has helped IT teams identify risks early, generate recommendations, and surface issues before they impact production. By linking operational intelligence with everyday tools, it has enabled teams to move from reactive troubleshooting to proactive operations.
How organizations use Red Hat Lightspeed today, however, has grown far beyond its original scope. Across industries, teams now consume Lightspeed data through custom dashboards, internal reporting portals, and IT service management (ITSM) platforms using the Lightspeed APIs. Others embed Lightspeed intelligence directly into CI/CD pipelines, observability stacks, and automated remediation workflows—turning insights into immediate, repeatable action.
In 2025, this vision has expanded even further. Authentication has been modernized, integrations have matured, and new event-driven and AI-enabled pathways now make it possible to progress beyond simple alerting toward intelligent, closed-loop remediation. In these workflows, Lightspeed findings don’t just inform humans—they directly trigger automated responses across your automation and monitoring ecosystem.
This article highlights what’s new: service account authentication, deeper integrations, Event-Driven Ansible, and the introduction of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server—capabilities designed to securely connect insight with action.
Secure and scalable API access enabled through service account–based authentication
Red Hat Lightspeed has introduced a modern API authentication model based on service accounts and access tokens, significantly improving both security posture and automation readiness.
Earlier integrations depended on user-based credentials and basic authentication. While adequate at the time, this approach limited scalability and made it harder to enforce consistent access controls across systems. Basic authentication has now been deprecated, reinforcing a shift toward token-based access designed for automation at scale.
With service accounts, integrations can authenticate using bearer tokens without requiring an interactive user session. This aligns with Red Hat’s broader strategy for secure, headless automation across hybrid and multicloud environments.
Why this matters
Stronger security controls. Tokens are associated with service accounts rather than individuals, reducing exposure of personal credentials. Access can be centrally managed, scoped, or revoked through the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console.
Automation-first design. Tokens can be generated and rotated programmatically, making it easier to integrate Lightspeed with CI/CD systems, monitoring platforms, and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform workflows.
Consistency at scale. Because service accounts are independent of user lifecycle changes, integrations remain stable across teams, environments, and long-running automation processes.
Enabling advanced integrations, Token-based authentication underpins newer capabilities such as the Lightspeed MCP server, allowing secure, agent-based access to Lightspeed data for AI-driven and event-based workflows.
The updated Lightspeed API documentation includes practical examples for authenticating with service accounts and bearer tokens, helping teams build automated workflows that retrieve inventory data, query vulnerabilities, or integrate with third-party tools such as Splunk and ServiceNow.
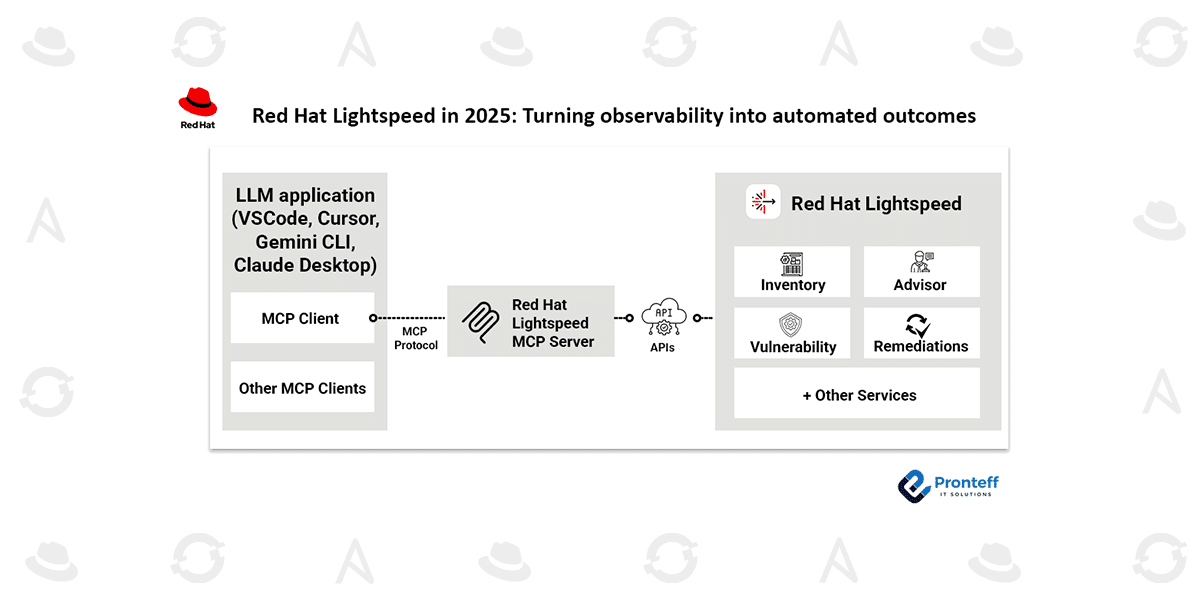
Introducing the MCP server: Bridging Red Hat Lightspeed with AI-powered workflows
One of the most significant updates in 2025 is the introduction of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, which extends Red Hat Lightspeed into the emerging world of agent-based and AI-assisted operations.
MCP provides a standardized interface that allows AI agents and automation systems to interact with external services through structured, predictable APIs—without requiring custom integrations for every tool.
Using MCP with Red Hat Lightspeed
Through the MCP server, core Lightspeed capabilities—such as system inventory, advisor recommendations, and vulnerability data—are exposed in a format that AI agents can easily consume. This allows intelligent systems to reason over Lightspeed findings and initiate actions with appropriate context and security controls.
A typical workflow might look like this:
A vulnerability is detected by Lightspeed → structured data is exposed via MCP → an AI agent evaluates severity and impact → an incident is opened in ServiceNow, and a remediation playbook is triggered through Ansible Automation Platform.
By adopting MCP, Red Hat is laying the foundation for deeper interoperability across its automation and observability portfolio, positioning Lightspeed not just as an analytics engine, but as an active participant in AI-driven decision-making and response.
Broader integrations across ITSM, observability, and automation
Red Hat Lightspeed continues to expand how it integrates with the tools that operations teams rely on daily. These integrations have evolved from basic data exports into context-aware automation touchpoints that bridge detection, visibility, and remediation.
ServiceNow flow templates
The latest certified ServiceNow application for Lightspeed introduces reusable flow templates that simplify ITSM automation. These templates enable teams to:
- Automatically create, enrich, or resolve incidents based on new or remediated Lightspeed findings
- Maintain a consistent system of record by linking recommendations to configuration items in the CMDB
- Customize workflows to align with internal change management and escalation policies
Splunk application enhancements
Updates to the Splunk application improve how Lightspeed data is ingested, visualized, and correlated with broader observability signals. Enhancements include:
- Richer event ingestion for advisor recommendations and vulnerability data
- Updated dashboards showing trends across compliance, patch exposure, and security posture for Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems
- Integration with Splunk alerts and workflows to support prioritization and response
By correlating Lightspeed insights with metrics and logs, teams gain a more complete view of system health across hybrid environments.
PagerDuty integration
The integration with PagerDuty enables real-time alerting when Lightspeed detects critical risks. Findings such as high-severity vulnerabilities or configuration drift can immediately generate incidents, complete with contextual details.
Custom routing and escalation policies allow organizations to align Lightspeed alerts with existing on-call and response processes.
Event-Driven Ansible collection
The Event-Driven Ansible collection for Red Hat Lightspeed enables fully automated remediation triggered directly by Lightspeed events. Common use cases include:
- Applying patches when vulnerabilities are detected
- Restarting services or enforcing configurations when drift occurs
- Updating CMDB records or audit logs after remediation
This event-driven approach reduces manual effort and accelerates response times, turning detection into immediate action.
Satellite and Ansible Automation Platform integrations
For organizations managing RHEL environments at scale:
- Integration with Red Hat Satellite surfaces insights directly within the Satellite interface, helping administrators plan and prioritize remediation.
- Integration with the Ansible Automation Platform connects detected issues to executable playbooks, allowing remediation to be launched directly from automation workflows.
Together, these integrations create a streamlined path from detection to resolution.
Bringing it all together
With these capabilities, operations teams can embed Red Hat Lightspeed deeply into their daily workflows—connecting intelligence, visibility, and automation across platforms.
In practice, organizations are combining these integrations to enable:
- ITSM automation: Lightspeed findings generate and update ServiceNow incidents linked to affected systems
- Unified visibility: Insights flow into Splunk dashboards for correlation with performance and security trends
- Proactive alerting: Critical risks trigger PagerDuty notifications for immediate response
- Automated remediation: Event-Driven Ansible playbooks resolve known issues without manual intervention
- AI-assisted operations: MCP-enabled agents analyze Lightspeed data and initiate informed actions
Together, these workflows transform Red Hat Lightspeed into a central decision hub—bridging people, processes, and platforms across hybrid environments.
Looking ahead
The integration ecosystem around Red Hat continues to evolve alongside advances in automation, observability, and AI. With service account authentication, event-driven automation, and MCP-based integrations, Lightspeed is becoming an increasingly powerful engine for connecting insight to action.
As new use cases emerge—across ITSM platforms, monitoring tools, and intelligent automation frameworks—Red Hat will continue to expand how Lightspeed fits into real-world operational workflows.
The objective remains clear: empower operations teams to securely convert Lightspeed recommendations into automated, reliable outcomes, enabling proactive IT operations that move confidently from insight to action.