OpenShift Toolkit 1.0 – Enhance cloud-native application development in IDEs
A developer needs a variety of toolkits like OpenShift Toolkit 1.0 to build, test, and deploy cloud-native applications. Developers now control the decision-making process and have the power of choice. In order to provide integrated value to our developer community, Red Hat must embrace this continuity.
Today, we’re happy to announce the updated OpenShift Toolkit 1.0 extension by Red Hat, a set of extensions for Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ that seeks to make it easier for developers to work with OpenShift and Kubernetes. Consequently, developer tools are made available at all times, starting with the IDE and a quicker Kubernetes development workflow.
It can take a long time for a developer to code on an IDE, switch between terminals, and install the necessary dependencies to run the code on OpenShift. A delayed inner loop is the result of this. With the help of this IDE extension, we hope to enhance the OpenShift inner loop experience by enabling quick local application development. We have focused on offering a variety of methods to optimize the developer workflow when dealing with your apps and deployment on the cloud running on OpenShift or Kubernetes with this 1.0 release of OpenShift Toolkit (earlier known as OpenShift Connector).
Without having to leave your IDE, the OpenShift Toolkit expands Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ to offer all of the functionality and convenience of IDEs for creating cloud-native Kubernetes applications. For a developer to test, debug, and deploy local code on an OpenShift instance without worrying about the challenges presented by various K8s tools. With the help of this extension, developers can quickly onboard to OpenShift application development and conduct all of these tasks with ease, allowing them to concentrate on creating the application rather than setting up and configuring various tools.
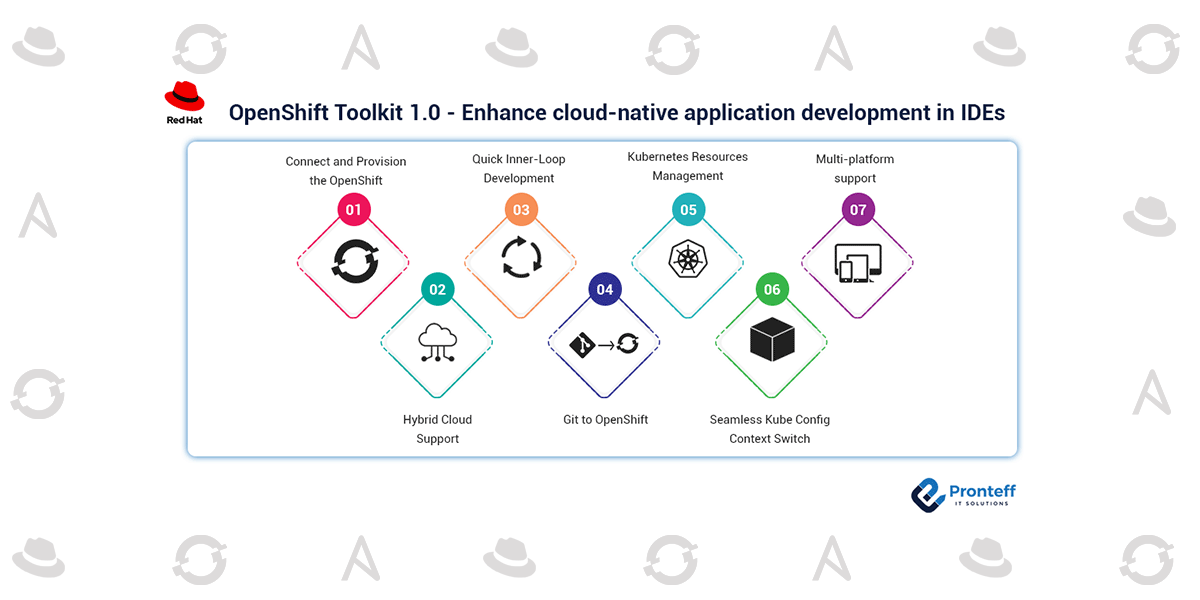
Developers can improve the workflow in the following ways with OpenShift Toolkit:
1. Connect and provision the OpenShift:
As developers, we already have the code ready in our local workspace. We require an instance of OpenShift to test, build and deploy the code in order to begin developing cloud-native apps. No longer is it necessary to exit the IDE and search for the cluster. With the help of a guided UI workflow inside the IDE, the OpenShift Toolkit enables the provisioning of an OpenShift cluster both locally using OpenShift Local and in the cloud using Red Hat Developer Sandbox.
2. Hybrid Cloud Support:
Developers can connect to any OpenShift instance that is active, including OpenShift Local, Red Hat OpenShift on AWS, Azure Red Hat OpenShift, and Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift, using this extension (30 days free-tier).
3. Quick Inner-Loop Development:
With the help of this plugin, a developer can create apps using either a local workspace, a git repository, or the built-in devfile templates. Developers may easily create components on the cluster and launch them in development mode with a one-click solution, syncing any changes occurring in real-time on the cluster. Get applications from the source to the workload as a result in minutes.
4. Git to OpenShift:
Using the extension’s suggested deployment approach, you can quickly and easily deploy the code from your git repository to OpenShift.
5. Kubernetes Resources Management:
Developers have access to pod, deployment, and deployment configuration logs as well as the ability to examine and update resources YAML manifests. Users of the extension can also access these resources using the cluster dashboard.
6. Seamless Kube Config Context Switch:
From the extension view, developers may work with apps in different Kubernetes contexts and switch between them as needed. They are able to run apps in the same way in the development and in the production environment as a result.
7. Multi-platform support:
macOS with arm64 support, Windows, and Linux are supported
Both the JetBrains Marketplace and the Visual Studio Code Marketplace offer the Toolkit for download. Please get in touch with us for feature requests and GitHub discussions as the code is open-source.
With OpenShift Toolkit serving as the recipe, we hope to enhance the cloud-native developer experience on OpenShift while still letting you use your preferred development tools. Start using the OpenShift Toolkit to create for OpenShift right away, and send us your comments.