Part 1: Delivering High-Precision Clock Synchronization for 5G Networks
With the arrival of 5G networks Mobile deployments worldwide, various vertical sectors (e.g. automotive, media and entertainment, public safety, amongst others) are looking ahead to take benefit of the numerous capabilities 5G networks have promised to deliver.
One of the protocols that play a vital position in unlocking such low-latency in 5G deployments is the IEEE 1588-2008 standard, which is likewise referred to as the Precision Time Protocol (PTP). In that direction, Red Hat has completely supported this generation for the reason for the launch of RHEL7.
In Telco 5G environments, the usage of this protocol is especially applicable while deploying Radio Access Networks (RAN). Consequently, we’ve got devoted this text to offering creation to this generation in a cloud-local O-RAN situation with the usage of OpenShift.
Let’s Jump right in
Currently, in Telco 5G deployments, the RAN additives may be synchronized with the use of various topologies. However, the O-RAN Specification WG4 has described 4 feasible configurations (i.e. LLS-C[1-4]) for synchronization of shipping fronthaul networks.
For the sake of simplicity, in this article, we’ve centered on imparting PTP profiles to synchronize the fronthaul shipping community with the use of Full Timing Support (FTS) in an LLS-C2 configuration. However, the PTP operator also can be configured to meet synchronization necessities withinside the different described configurations.
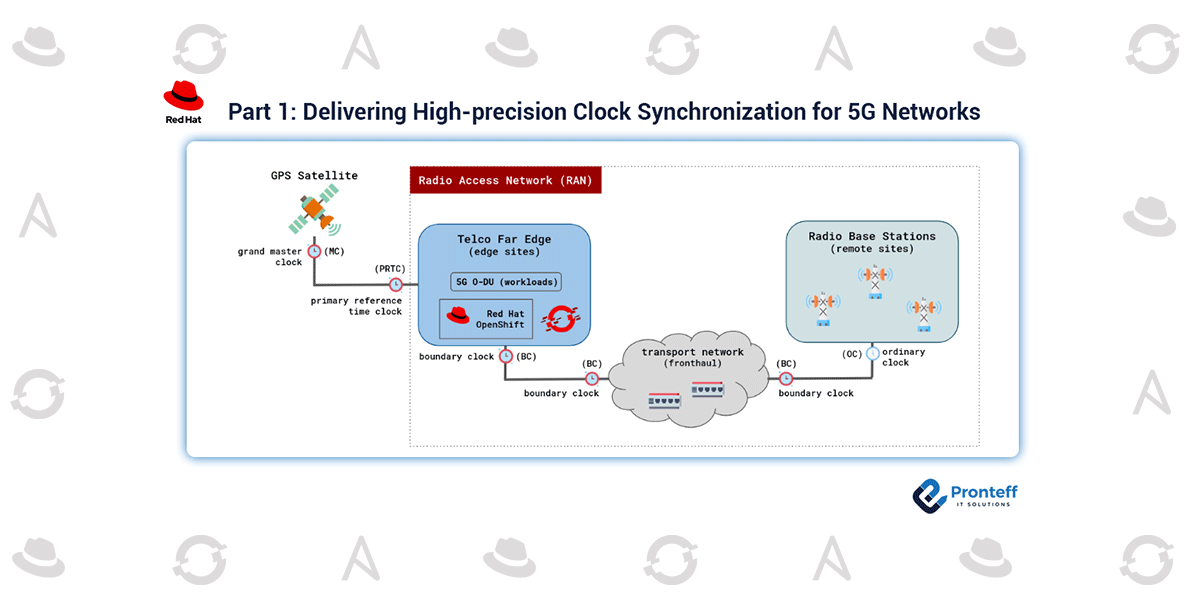
In above Figure 1, a high-degree synchronization configuration of the use of OpenShift in a cloud-local 5G RAN situation is presented.
Typically, in a PTP hierarchy we can also additionally discover the subsequent high-degree components:
Grandmaster (GM) clock:
This is the number one reference time clock (PRTC) for the complete PTP community. It commonly synchronizes its clock from an outside GPS supply. However, if missing, it may additionally use some other NTP server as a time reference.
Boundary clock (BC):
This intermediate tool has a couple of PTP-successful community connections to synchronize one community phase to some other accurately. It synchronizes its clock to a grasp and serves as a time supply for everyday clocks. On the occasion of dropping its grasp, it is able to end up the brand new grandmaster clock withinside the PTP community.
Ordinary clock (OC):
By evaluating to boundary clocks, this tool most effectively has an unmarried PTP-successful community connection. It additionally synchronizes its clock to a grasp and might end up grandmaster if no different is appearing as such withinside the PTP community.
FRONTHAUL TRANSPORT NETWORK
The fronthaul delivery community is anticipated to distribute high-precision time and frequency synchronization from a 5G virtualized Distributed Unit (DU), appearing as a grandmaster, jogging on OpenShift at an area site, to each regular clock positioned in RUs on the far-off sites.
Ideally, community devices (i.e. switches, etc.) enforcing the fronthaul delivery community must be configured as BC. This situation is described with the aid of using the ITU-T profile G.8275.1 and called Full Timing Synchronization (FTS). This situation is strongly advocated for a gold standard O-RAN operation with fine accuracy results.
However, FTS configurations are probably highly-priced for huge networks. Hence, while now no longer all of the community device enforcing the fronthaul phase helps PTP, we’re withinside the face of a Partial Timing Synchronization (PTS) situation, described additionally with the aid of using ITU-T withinside the G.8275.2 profile.
For PTS scenarios, OpenShift additionally gives an opportunity to fill this gap. On the only hand, it wishes to be configured as BC. On the other, the switches that behave as passive factors must be configured to keep away from filtering MAC PTP multicast frames. This may be clearly performed with the aid of using permitting the 01:1B:19:00:00:00 multicast MAC to cope with by skipping via all of the switches’ interfaces.
An appearance in the PTP operator
As with each day 2 operator in OpenShift, the lifecycle of the PTP operator may be without difficulty controlled by the use of OLM. Even even though this operator handles cluster-extensive PTP configurations, it’s miles a namespaced operator.
Hence, whilst deploying it thru the CLI, growing a namespace alongside an operator institution and subscription items is recommended. If with the aid of using contrast, you’ll choose a greater pleasant interface just like the OpenShift internet console, a system is likewise to be had to acquire so.
Once the PTP operator is going for walks at the cluster nodes in which the O-RAN workloads may be hosted, we come to a topology just like the one supplied in Figure 2.
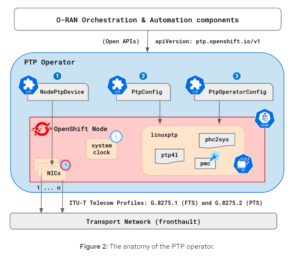
As proven withinside the figure, the PTP operator gives 3 Custom Resource Definition (CRD) objects, particularly NodePtpDevice, PtpConfig, and PtpOperatorConfig sources. We will discover those sources deeply and offer a few CRs for not unusual place PTP profiles withinside the following sections of this article.
These custom API sources offer a declarative approach, for the configuration of PTP profiles, to outside additives withinside the O-RAN Orchestration and Automation layer. Additionally, the PTP operator additionally deploys a linuxptp daemon with the PTP programs required to use required Telecom profiles.
Specifically, NodePtpDevice is chargeable for coming across PTP-successful community gadgets for your cluster nodes. Meanwhile, the PtpConfig and PtpOperatorConfig sources once engage with the Linux PPP programs to well follow PTP configurations.