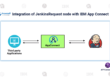
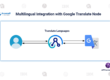
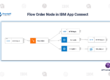
Road Map Of IBM APP Connect Enterprise
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 12.0.3.0
Test-driven development
The new test-driven development feature facilitates the adoption of agile practices while mitigating risks, enabling developers to iteratively test as they develop and automate test authoring
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 12.0.2.0
Improved toolkit UI
The upgraded IBM App Connect Enterprise Toolkit features a modernized look and feel that increases development productivity by simplifying the creation of message flows and message models from scratch.
Business Transaction Monitoring
The new Business Transaction Monitoring capability introduced in 12.0.2.0 enables you to get the best out of your business transactions, by monitoring the end-to-end lifecycle of your enterprise transactions.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 12.0.1.0
New Tutorials Interface
The newly-designed tutorial interface includes over 100 tutorials to easily get started and rapidly familiarize with IBM App Connect Enterprise, reducing the onboarding time. This includes guides on how to create an integration server, message flows, unit tests, and many more.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.15
Simplicity and productivity
Flexible administrative control over integration servers and resources
IBM Integration Bus provided an integration node component as the central point of administrative control over a set of owned integration servers. IBM App Connect Enterprise Version 11.0 provides support for integration servers that can be created and run independently from an integration node, so you can deploy your applications to an integration server quickly and easily, without the need to create and configure an integration node.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.14
Plug-in Development perspective
You can use the Plug-in Development perspective to create user-defined node projects and user-defined nodes in the IBM® App Connect Enterprise Toolkit, however, the preferred option is to use the Integration Development perspective.
If version or custom keyword information was added to your resources during development, you can view the values in resources that are deployed to an integration server.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.13
Security is an important consideration for both developers of IBM® App Connect Enterprise applications, and for system administrators configuring IBM App Connect Enterprise authorities.
When you are designing an IBM App Connect Enterprise application, it is important to consider the security measures that are needed to protect the information in the system.
The Security Overview introduces the concepts that you need to understand before you set up security for IBM App Connect Enterprise.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.12
IBM App Connect Enterprise provides a security manager to control access to individual messages in a message flow, by using the identity of the message.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.11
In IBM App Connect Enterprise message flow security, authentication involves the security manager either passing the identity type and token to an external security provider or checking the identity by using credentials stored locally in the integration server’s vault.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.10
IBM App Connect Enterprise provides support for identity mapping (also known as identity federation) and token issuance and exchange. Identity mapping is the process of mapping identity in one realm to another identity in a different realm
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.9
You can use patterns to create integrated solutions. Patterns provide reusable solutions that encapsulate a tested approach to solving a common architecture, design, or deployment task in a particular context
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.8
ACEv11 supports users migrating message flows deployed to previous versions of IIB using the mqsi extract components command. Message flows with UDPs defined, will run in ACEv11 as they did in previous versions. However, when using the administrative REST API to GET information about the deployed message flow, these UDPs will not be reported in the response sections named “userDefinedProperties” and “active”->”userDefinedProperties”. New UDP values which are updated using the “apply-global-udp-override” action are correctly reported.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.7
Parsers
A parser is a program that interprets the physical bitstream of an incoming message and creates an internal logical representation of the message in a tree structure. The parser also regenerates a bitstream for an outgoing message from the internal message tree representation.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.6
Each message that flows through an integration node has a specific structure that is meaningful to the applications that send or receive that message.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.5
A bend point is added to a connection between two message flow nodes where the line that represents the connection changes direction.
Use bend points to change the visual path of a connection to display node alignment and processing logic more clearly and effectively. Bend points have no effect on the behavior of the message flow; they are visual modifications only.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.4
Message Flow terminals
Use terminals to control the route that a message takes, depending on whether the operation that is performed by a node on that message is successful. Terminals are wired to other node terminals by using message flow node connections to indicate the flow of control.
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.3
MRM Parser and Domain
The MRM domain can be used to parse and write a wide variety of message formats. It is primarily intended for non-XML message formats, but it can also parse and write XML
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.2
Data Conversion
Convert data that your message flows are transferring between different environments by using IBM® MQ or IBM App Connect Enterprise facilities
IBM APP Connect Enterprise 11.0.0.1
Processing Events
You can use event-driven message processing to control the flow of messages through your message flows, by using aggregation, message collections, message sequences, and timeout flows.