Security Features in Azure Red Hat OpenShift
Securing scaling of your cloud environments is crucial when your company updates its cloud technology. Your security requirements are supported at scale by Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO). Red Hat and Microsoft are jointly responsible for ARO, which can assist your company in enhancing cloud security in a number of ways.
Your firm may streamline software deployment and lower operational complexity with automatic security maintenance and continual monitoring thanks to ARO’s built-in security features. Red Hat’s Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) team automates, controls, and watches over your platform so your company can concentrate on tasks that add value rather than having to worry about manually installing patches and security upgrades. In the words of our SRE teams, “We make infrastructure boring.”
We have deployed a number of new security measures as part of our ongoing efforts to raise consumer security standards.
Upgrades and vulnerabilities in cyberspace
The advantages of the work done by the Red Hat Security team are available to customers. The Red Hat security team examines CVEs, assesses their seriousness, and, if necessary, offers errata. Based on analysis by Red Hat Engineering, Red Hat Errata aids users in determining what updates are available and their significance. A version upgrade that can be applied to the clusters manually or automatically using tooling included with Azure Red Hat OpenShift will contain the majority of these errors. The freshly launched Managed Upgrade Operator is used by the automated process.
All you need to do to set up the operator is apply a YAML file with a planned time for the update to happen; the operator will take care of the rest. Consult this page for more information on how to configure the operator.
Upgrades to the cluster configuration
On putting security best practices into effect, we frequently collaborate with Microsoft and customer security teams.
Storage and Egress Lockdown are two recently announced features that were developed in response to user and Microsoft input.
The storage accounts now have more protection thanks to Storage Lockdown. This was accomplished by upgrading the storage account’s configuration to require the use of a newer storage account version and a higher TLS version. Additionally, it verifies that encryption is activated and that the storage account is private. All users of Azure Red Hat OpenShift can access this capability. Study up on storage lockdown.
Additionally, we heard from customers who wished to reduce their reliance on Egress traffic despite the fact that private clusters were private (no ingress was permitted). The main objective of this dependence was to enable communication between the cluster and Azure endpoints (for example to the Azure container registry). For minimum deployment scenarios, clusters can be installed without a link to the Internet thanks to a private endpoint we developed to increase the security of these deployments. You’ll see in the figure below [1] that the cluster has access to the service through a private endpoint. Exclusive access to the specific resources that the cluster depends on is provided via this private endpoint.
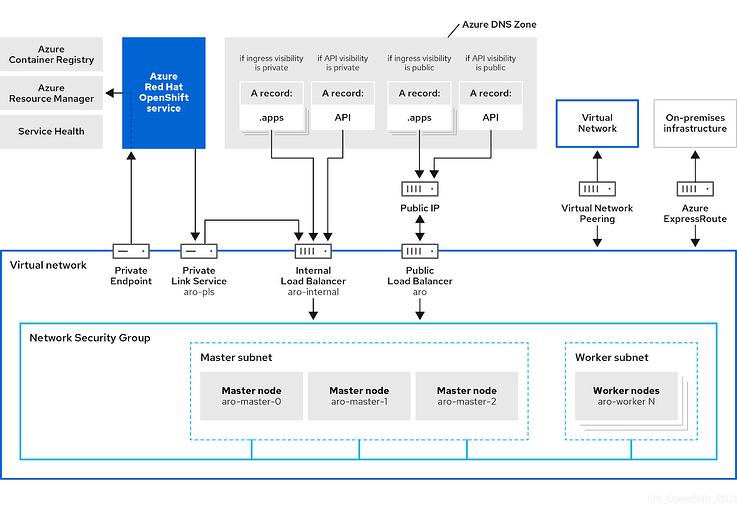
Figure 1 shows the Azure Red Hat OpenShift network topology.
Some users may choose to connect to additional registries or external resources; in some use situations, this may be advised since they can give users access to more Red Hat Operators. However, traffic from these external resources would go through the VNet peering and Azure Express route. Study up on Egress Lockdown.
Requirements and certificates
Customers who use Azure Red Hat Openshift benefit from Azure’s and Red Hat’s compliances, which together offer a wide range of alternatives. Microsoft Azure provides a variety of compliance solutions. We have various certifications in their cloud, including PCI DSS, FedRAMP, HIPAA, and many more, thanks to our partnership with Microsoft Azure. Find out more about these on the Azure compliance website.
Red Hat also offers a comprehensive set of compliance tooling for extra security requirements. On Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management offers management and controls via built-in policies that may be applied. An additional native layer of security is provided for apps running on the platform by Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security (ACS) for Kubernetes.